Chapter: Orthopaedics
Orthopaedics: Hip
Hip
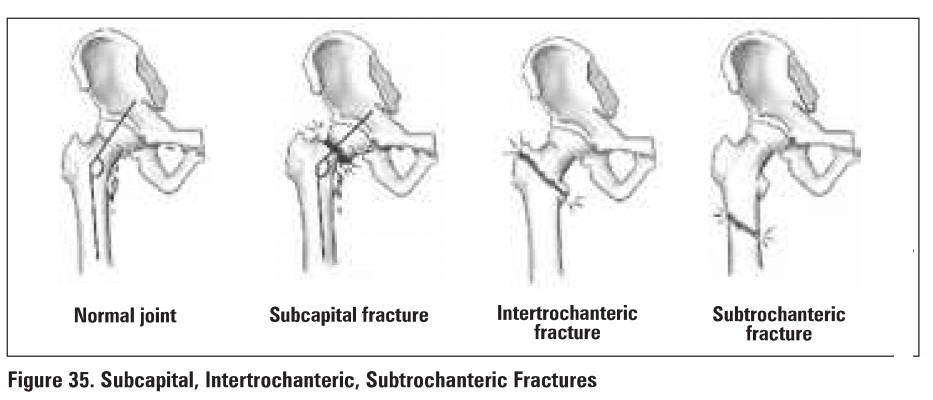
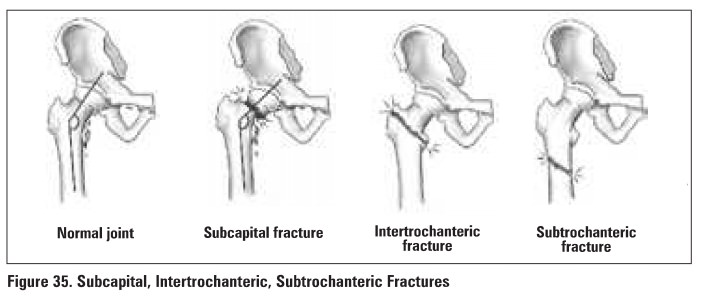
Hip Fracture
General Features
·
acute onset of hip pain
·
unable to weight-bear
·
shortened and externally rotated leg
·
painful ROM
Arthritis of the Hip
Etiology
·
osteoarthritis (OA), inflammatory arthritis,
post-traumatic arthritis, late effects of congenital hip disorders or septic arthritis
Clinical Features
·
pain (groin, medial thigh) and stiffness
aggravated by activity
·
morning stiffness, multiple joint swelling, hand
nodules (RA)
·
decreased ROM (internal rotation is lost first)
·
crepitus
·
± fixed flexion contracture leading to apparent
limb shortening (Thomas test)
·
± Trendelenberg sign
Investigations
·
x-ray
o
OA: joint space narrowing, subchondral sclerosis,
subchondral cysts, osteophytes
o
RA: osteopenia, joint space narrowing, subchondral
cysts
·
bloodworic ANA, RF
Treatment
·
conservative: weight reduction, activity
modification, PT, analgesics, walking aids
·
operative: realign = osteotomy; replace =
arthroplasty; fuse = arthrodesis
·
complications with arthroplasty: component
loosening, dislocation, heterotopic bone formation, thromboembolus, infection,
neurovascular injury
·
arthroplasty is standard of care in most patients
with hip arthritis
Hip Dislocation after THA
Etiology
·
total hip arthroplasty (THA) that is unstable when
hip is flexed, adducted and internally rotated or extended and externally
rotated (avoid flexing hip >90 degrees or crossing legs for approximately 6
weeks after surgery)
Epidemiology
·
occurs in 1-4% of primary THA and 10-16% of
revision THAs
·
risk factors: neurological impairment,
post-traumatic arthritis, revision surgery, substance abuse
Treatment
·
external abduction splint to prevent hip adduction
·
constrained acetabular component for recurrent
dislocation if no issue with position of acetabular/femoral implants
Complications
·
sciatic nerve palsy in 25% (10% permanent)
·
heterotopic ossification (HO)
Related Topics