Chapter: Orthopaedics
Orthopaedics: Knee
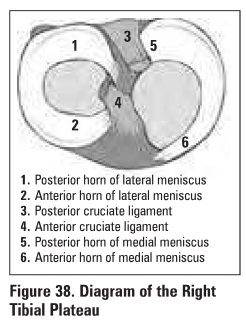
Knee
Evaluation of Knee Complaints
History
·
general orthopaedic history
·
also inquire: about common knee symptmns
o
locking: mechanical block to extension
o
–torn meniscus/loose body in joint
o
pseudo-locking: limited ROM without mechanical
block
o
–effusion, muscle spasm after injury, arthritis
·
painful clicking (audible)
o
torn meniscus
·
giving way: instability
o
cruciate ligament or meniscal tear, patcllar
dislocation
Physical Examination
·
general orthopaedic physical exam (do not forget to
evaluate hip)
Special Tests of the Knee
·
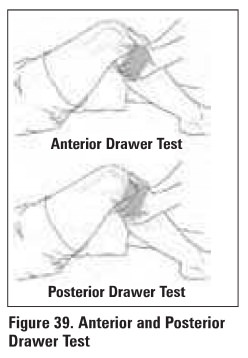
Anterior
and Polter.lor drawer tests (see Figure 39)
o
demonstrate tom ACI. and PCI., respectively
o
knee flexed at 900, foot immobilized, hamstrings
released
o
if able to sublux tibia anteriorly, then ACL may
be torn
o
if able to sublux tibia posteriorly, then PCL may
be torn
·
Lachmann test
o
demonstrates torn ACL
o
hold knee in 10-20" fleJ:ion, stabilizing the
femur
o
try to sublux tibia anteriorly on femur
o
similar to anterior drawer test, more reliable due
to less muscular stabilization
·
Posterior
sag lip
o
demonstrates tom PCI.
o
may give a false positive anterior draw sign
o
flex: knees and hips to 90", hold ankles and
knees
o
view from the lateral. aspect
o
if one tibia sags posteriorly compared to the
other, its PCL Is tom
·
Pivot shift
sign
o
demonstrates torn ACL
o
start with the knee in atension
o
internally rotate foot, slowly flex knee while
palpeting and applying a valgus force
o
normal knee will flex: smoothly
o
if incompetent ACL, tibia willsublux anteriorly on
femur at 5tart of maneuver. During flexion, the tibia will reduce and extemally
rotate about the femur (the "pivot"')
o
reverse pivot 5hlft (start in flmon, mernally
rotate, apply valgus and mend knee) suggests torn PCI.
·
Collateral
ligament stress test
o
palpate ligament for •opening" of joint space
while testing
o
with knee in full extension, apply valgus force to
test MCL, apply VllrWI force to test LCL
o
repeat tcst5 with knee in 20" flexion to relax
joint capsule
o
opening only in 20° flexion due to MCL damage only
o
opening in 2° of flexion and full extension is due
to MCL, cruciate, and Joint capsule damage
Test for meniscal tear
·
Crouch compression test
o
joint line pain when squatting (anterior pain
suggests patellofemoral pathology)
·
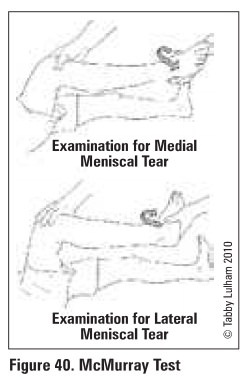
McMurray's test useful collaborative information
(see Figure 40)
o
with knee in flexion, palpate joint line for
painful "pop/click"
o
intemally robrte foot. varus stress, and extend
knee to test lateral menisCUll
o
externally rotate root, valgus stress, and extend
knee to test medial menisCUll
X-Rays
·
AP standing. lateral
·
skyline - tangential view with knees flexed at 45o
to see patellofemoral joint
·
3-foot standing view - useful in evaluating leg
length and varusfva1gus alignment
·
see Ottawa Knee Rules (Emergency Medicine, ERl7)
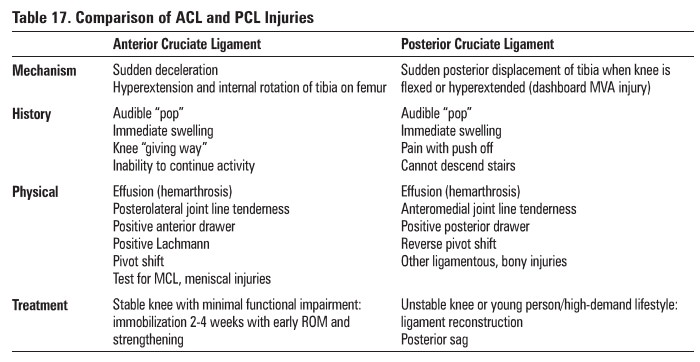
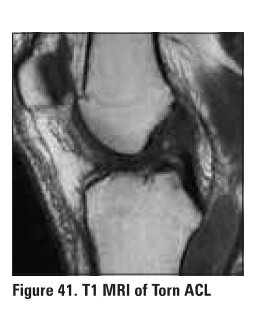
Cruciate Ligament Tears
·
ACL tear much more common than PCL tear
Collateral Ligament Tears
·
MCL tear more common than LCL tear
Mechanism
·
valgus force to knee =medial collateral ligament
·
varus force to knee =lateral collateral ligament
Clinical Features
·
swelling/effusion
·
tenderness above and below joint line medially
(MCL) or laterally (LCL)
·
joint laxity with varus or valgus force to knee
o
laxity with endpoint suggests partial tear
o
laxity with no endpoint suggests a complete tear
·
test for other injuries (e.g. O'Donahue's triad),
common peroneal nerve injury
Treatment
·
partial tear: immobilization x 2-4 weeks with
early ROM and strengthening
·
complete tear or multiple ligamentous inJuries:
surgtcal repair of ligamenta- not for MCL or LCL on their own
Maniacal Tears
·
medial tear much more common than lateral tear
Mechanism
·
twisting force on knee when it is partially flexed
(e.g. stepping down and turning)
·
requires moderate trauma in young person but only
mild trauma in elderly due to degeneration
Clinical Features
·
immediate pain, difficulty weight-bearing,
instability and clicking
·
increased pain with squatting and/or twisting
·
effusion (hemarthrosis) with insidious onset
(24-48 hrs after injury)
·
joint line tenderness medially or laterally
·
locking of knee (if portion of meniscus
mechanically obstructing extension)
Investigations
·
MRI, arthroscopy
Treatment
·
if not locked: ROM and strengthening
·
if locked or failed above: arthroscopic
repair/partial meniscectomy
Quadriceps/Patellar Tendon Rupture
Mechanism
·
sudden forceful contraction of quadriceps during
an attempt to stop
·
more common in obese patients and those with
pre-existing degenerative changes in tendon
o
DM, SLE, RA, steroid use, renal failure on
dialysis
Clinical Features
·
inability to extend knee or weight-bear
·
possible audible "pop"
·
patella in lower or higher position with palpable
gap above or below patella respectively
·
may have an effusion
Investigations
·
ask patient to straight leg raise
·
knee x-ray to rule out patellar fracture
·
lateral view: patella alta with patella tendon
rupture, patella baja with quadriceps tendon rupture
Treatment
·
non operative treatment for incomplete tears with
preserved extension of knee
·
surgical repair of tendon indicated for complete
ruptures
Dislocated Knee
Mechanism
·
high energy trauma
·
by definition, caused by tears of multiple
ligaments
Clinical Features
·
classified by relation of tibia with respect to femur
o
anterior, posterior, lateral, medial, rotary
·
knee instability
·
effusion
·
pain
·
ischemic limb
Investigations
·
x-rays: AP, lateral, skyline
o
associated radiographic findings include tibial
plateau fracture dislocations, proximal fibular fractures and avulsion of
fibular head
·
ankle brachial index (abnormal if less than 0.9)
·
arteriogram if abnormal vascular exam
Treatment
·
urgent closed reduction
o
complicated by interposed soft tissue
·
assessment of peroneal nerve, tibial artery; and
ligamentous injuries
·
repair of associated injuries; also may need
decompressive fasciotomy especially if vascular repair undertaken fasciotomy
·
knee immobilization x 6-8 weeks
Specific Complications
·
high incidence of associated injuries
o
popliteal artery tear
o
peroneal nerve injury
o
capsular tear
·
chronic: instability, stiffness, post-traumatic
arthritis
Related Topics