Chapter: Orthopaedics
Orthopaedics: Forearm
Forearm
Radius and Ulna Fracture
Mechanism
·
commonly a FOOSH or direct blow
Investigations
·
x-ray: 1) AP and lateral of forearm; 2) AP,
lateral, oblique of elbow and wrist
·
CT if fracture is close to joint
Treatment
·
goal is anatomic reduction since imperfect
alignment significantly limits forearm pronation and supination
·
ORIF with compresslon plates and screws
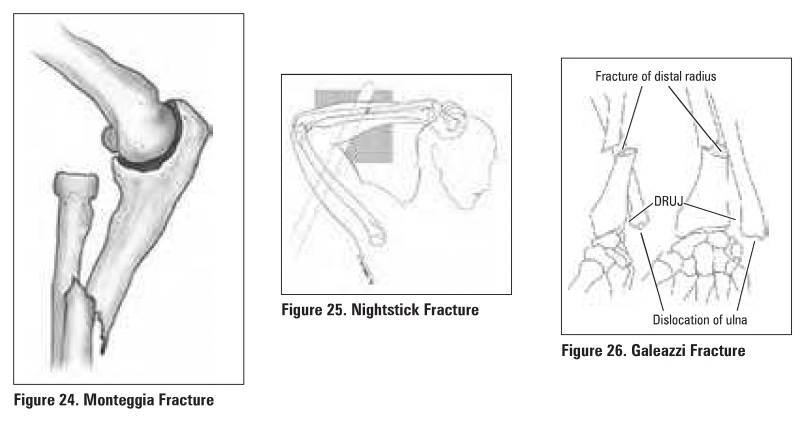
Monteggia Fracture
Definition
·
fracture of the proximal ulna with radial head dislocation
Mechanism
·
direct blow on the posterior aspect of the forearm.
·
hyperpronation
·
fall on the hyperextended elbow
Clinical Features
·
decreased rotation of forearm ± palpation lump at
the radial head
·
ulna angled apex anterior and radial head
dislocated anteriorly (rarely the reverie deformity occurs)
Treatment
·
ORIF of ulna with indirect radius reduction in 90%
·
splint and early post-op ROM if elbow completely
stable; otherwise immobilization in plaster with elbow flexed for 6 weeks
Specific Complications (see
General Fracture Complications)
·
compartment syndrome
·
radial/posterior interosseous nerve (PIN) injury
·
decreased ROM
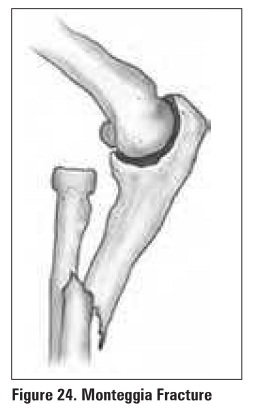
Nightstick Fracture
Definition
·
isolated fracture of ulna
Mechanism
·
direct blow to forearm (holding arm up to protect
face)
Treatment
·
non-displaced: below elbow cast (10 days) followed
by forearm brace (-8 weeks)
·
displaced: ORIF if >5096 shaft displacement or
>10° angulation
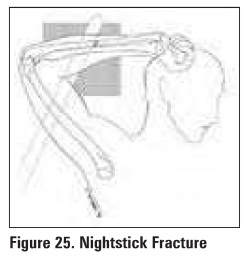
Galeazzi Fracture
Definition
·
fracture of the distal radial shaft with
disruption of the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ)
·
most commonly in the distall 1/3 of radius near
junction of metaphysis/diaphysis
Mechanism
·
usual cause is fall on the hand (mechanical axial
loading ofpronated forearm)
lnvestigations
·
x-rays
o
shortening of distal radius >5 mm relative to the
distal ulna
o
widening of the DRUJ space on AP
o
dislocation of radius with respect to ulna on true
lateral
Treatment
·
ORIF of radius
·
if DRUJ is stable, splint with early ROM
·
if DRUJ ill unstable, DRUJ pinning and long arm
cast in supination x 6 weeks
Related Topics