Chapter: Human Nervous System and Sensory Organs : Functional Systems
Motor End Plate
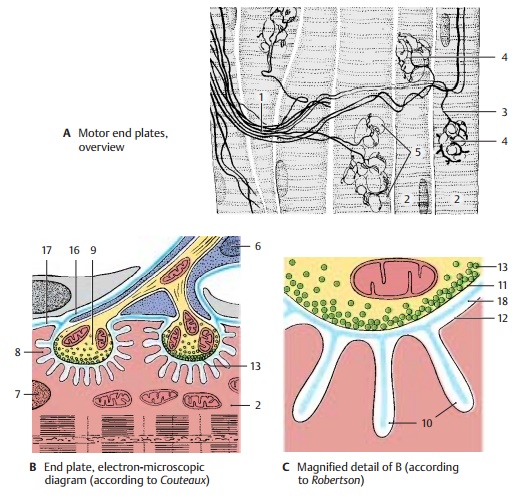
Motor End Plate
The
axons of the motor neurons (A1)
arborize in the muscles so that each muscle fiber (AB2) is reached by an axonal branch (A3). The number of muscle fibers supplied by one axon varies
considerably. While a single axon may innervate two to three muscle fibers in
the muscles of eyes and fin-gers, it may supply 50 – 60 muscle fibers in other
muscles. The anterior horn cell and its axon (α-motoneuron) together with the
group of muscle fibers it supplies is called a motor unit. When the neuron is stimulated,the muscle fibers
contract in unison. The terminal branches of the axon lose their my-elin
sheaths before terminating and form tangled ramifications. In the terminal
re-gion, the surface of the muscle fiber forms a flat eminence (hence the term end plate) (A4).
The area
of axonal arborization (A5)
con-tains a number of cell nuclei. The nuclei lying on top of the axonal
ramifications belong to Schwann cells that envelop the axon terminals (teloglia) (B6). The nuclei lying beneath the ramifications (B7) are muscle fiber nuclei in the
region of the end plate. At the junction between axoplasm and sarcoplasm, the
axon terminals are sur-rounded by a palisade layer (B8) which con-sists of infoldings of the sarcolemma, as shown by
electron microscopy.
The
axons terminate with boutonlike swell-ings (B9) that dip into the surface of the end plate. These grooves are
lined by the mem-brane of the sarcoplasm (sarcolemma) and a basement membrane.
The heavily folded sarcolemma of the grooves (subneural clefts) (C10)
greatly enlarges the surface area of the muscle fiber.
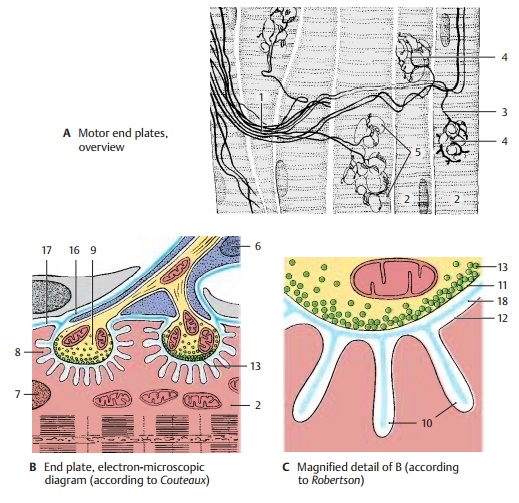
The
motor end plate is a specialized syn-apse. Its presynaptic membrane is the
axo-lemma (C11), and its
postsynaptic mem-brane is the folded sarcolemma (C12). The substance transmitting nerve impulses to the muscle fiber
is acetylcholine. It is con-tained
in clear synaptic vesicles (BC13).
Upon stimulation of the axon, the neu-rotransmitter is released into the
synaptic cleft, resulting in receptor-mediated (ni-cotinic acetylcholine receptors)
depolariza-tion of the membrane of the muscle fiber.
Related Topics