Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Michelson's method
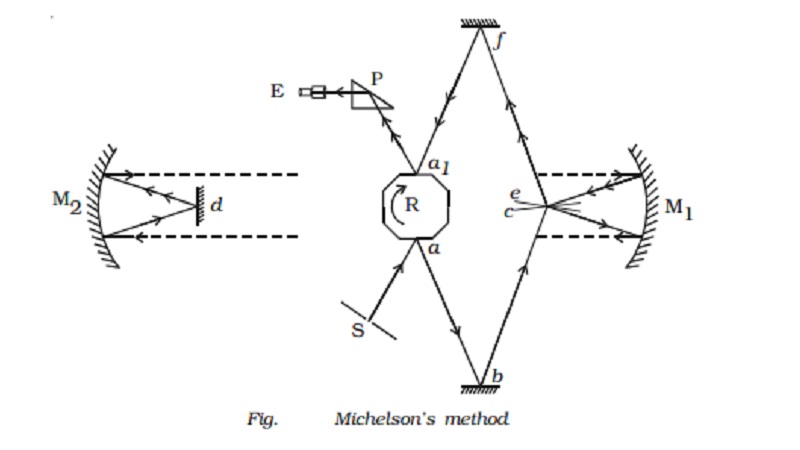
Michelson s method
A.A. Michelson, an
American physicist, spent many years of his life in measuring the velocity of
light and he devised a method in the year 1926 which is considered as accurate.
The experimental set
up is shown in Fig. . Light from an arc source after passing through a narrow
slit S is reflected from one face a of
an octagonal mirror R. The ray after reflections at small fixed mirrors b and c is then rendered
parallel by a concave mirror M1 placed in the observing station on
Mt. Wilson. This parallel beam of light travels a distance of 35 km and falls
on another concave mirror M2 placed at Mt. St Antonio, and it is
reflected to a plane mirror d placed
at the focus of the concave mirror M2. The ray of light from d is rendered parallel after getting
reflected by M2 and travels back to the concave mirror M1.
After reflections at M1
and the plane mirrors e and f, the ray falls on the opposite face a1 of the octagonal mirror.
The final image which is totally reflected by a total reflecting prism P, is
viewed through an eye piece E.
When the octagonal
mirror is stationary, the image of the slit is seen through the eye piece. When
it is rotated the image disappears. The speed of rotation of R is suitably
adjusted so that the image is seen again clearly as when R is stationary. The
speed of revolution is measured by stroboscope.
Let D be the distance travelled by light
from face a to face a1 and n be the number of rotations made by R per second.
The time taken by R to
rotate through 45o or 1/8 of
a rotation = 1/ 8n
During this time interval, the distance
travelled by the light = D
The velocity of light
c = Distance travelled / Time taken = D/(1/8n) = 8nD
In general, if the
number of faces in the rotating mirror is N,
the velocity of light = NnD.
The velocity of light
determined by him is 2.99797 ? 108 m s?1.
Importance of velocity
of light
The value of velocity
of light in vacuum is of great importance in science. The following are some of
the important fields where the value of velocity of light is used.
(1)
Frequency - wavelength relation : From the relation c = ν, the
frequency of electromagnetic radiations can be calculated if the wavelength is
known and vice versa.
(2)
Relativistic mass variation with velocity : Theory of relativity has shown that the mass m of a moving particle varies with its
velocity v according to the relation m = m0/root[1-(v2/c2)]
Here mo is the
rest mass of the particle.
(3)
Mass - Energy relation : E = mc2 represents conversion of mass into energy and energy into mass.
The energy released in nuclear fission and fusion is calculated using this
relation.
(4)Measurement of large
distance in Astronomy : Light year is
a unit of distance
used in astronomy. A light year is the distance travelled by light in one year.
It is equal to 9.46 ? 1015 metre.
(5) Refractive index : The refractive index ? of a medium is given
by ? = velocity of light in vacuum /
velocity of light in medium = c/v
Related Topics