Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 3 : Periodic Classification of Elements
Mendeleev's Classification
Mendeleev's
Classification
In 1868, Lothar Meyer had developed a table of the
elements that closely resembles the modern periodic table. He plotted the
physical properties such as atomic volume, melting point and boiling point
against atomic weight and observed a periodical pattern.
During same period Dmitri Mendeleev independently proposed
that “the properties of the elements are the periodic functions of their atomic
weights” and this is called periodic law. Mendeleev listed the 70 known
elements at that time in several vertical columns in order of increasing atomic
weights. Thus, Mendeleev constructed the first periodic table based on the
periodic law.
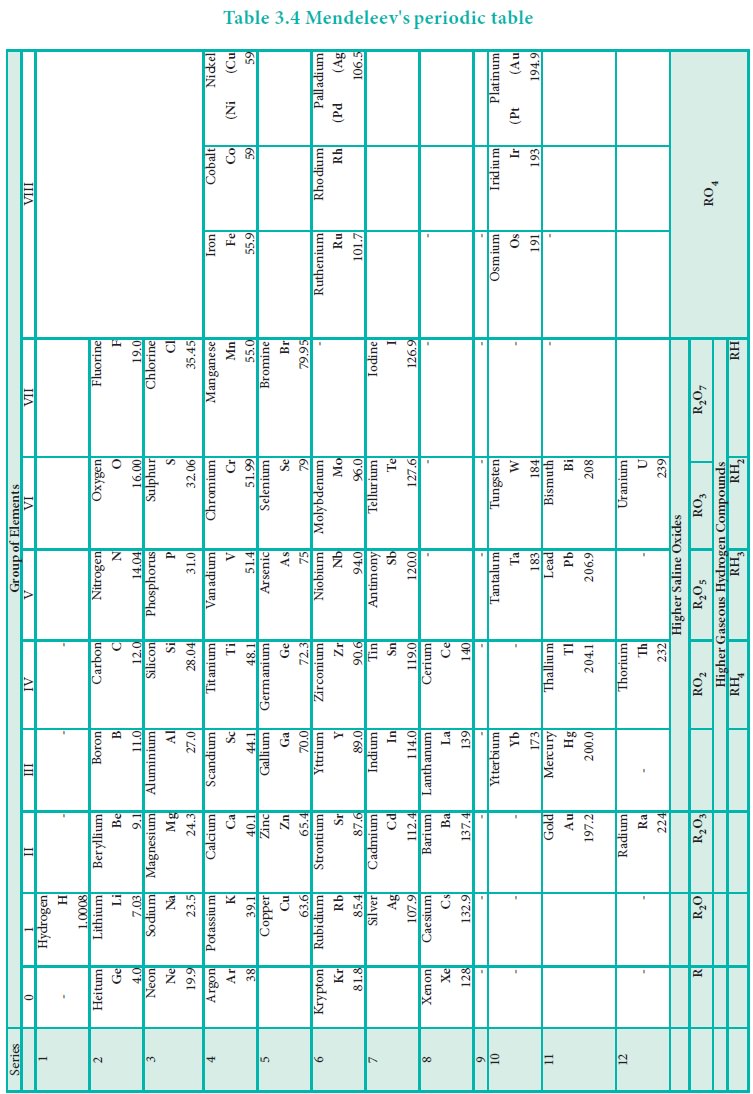
As shown in the periodic table, he left some blank spaces
since there were no known elements with the appropriate properties at that
time. He and others predicted the physical and chemical properties of the
missing elements. Eventually these missing elements were discovered and found
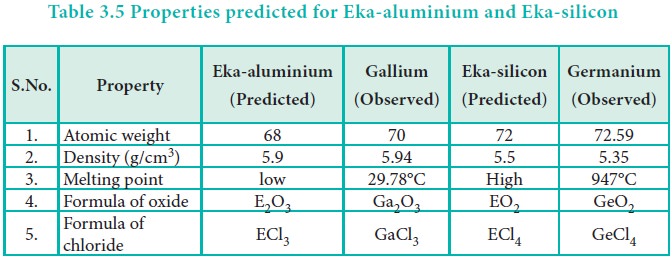
to have the predicted properties. For example, Gallium (Ga) of group and
germanium (Ge) of group IV were unknown at that time. But Mendeleev predicted
their existence and properties. He referred the predicted elements as
eka-aluminium and eka-silicon. After discovery of the actual elements, their
properties were found to match closely to those predicted by Mendeleev (Table
3.4 ).
Anomalies of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
Some elements with similar properties were placed in
different groups and those with dissimilar properties were placed in same
group.
Example: Tellurium (127.6) was placed in VI group but
Iodine (127.0) was placed in VII group.
Similarly elements with higher atomic weights were placed
before lower atomic weights based on their properties in contradiction to his
periodic law. Example 59Co27 was placed before 58.7Ni28
Related Topics