Solved Example Problems - Evaluate Yourself: Chemistry Periodic Classification of Elements | 11th Chemistry : UNIT 3 : Periodic Classification of Elements
Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 3 : Periodic Classification of Elements
Evaluate Yourself: Chemistry Periodic Classification of Elements
Evaluate Yourself
1. What is the basic difference in
approach between Mendeleev's periodic table and modern periodic table ?
2. The element with atomic number
120 has not been discovered so far. What would be the IUPAC name and the symbol
for this element? Predict the possible electronic configuration of this
element.
Answers:
Atomic number : 120
IUPAC temporary symbol : Unbinilium
IUPAC temporary symbol : Ubn
Possible electronic configuration :[Og] 8s2
3. Predict the position of the
element in periodic table satisfying the electronic configuration (n-1)d2,
ns2 where n=5
Answers:
Electronic Configuration : (n –
1)d2 ns2
for n = 5, the electronic
configuration is,
1s22s2 2p6
3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 4d2
5s2Atomic number : 40
4th group 5th
period (d block element)
= Zirconium
4. Using Slater's rule calculate
the effective nuclear charge on a 3p electron in aluminium and chlorine.
Explain how these results relate to the atomic radii of the two atoms.
Answers:
Electronic Configuration of Aluminium
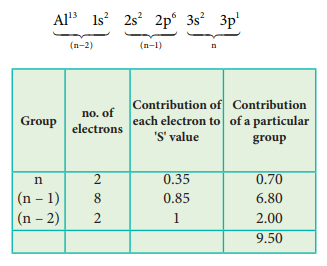
Effective nuclear charge = Z – S
= 13 – 9.5
(Zeff)Al = 3.5
Electronic Configuration of chlorine
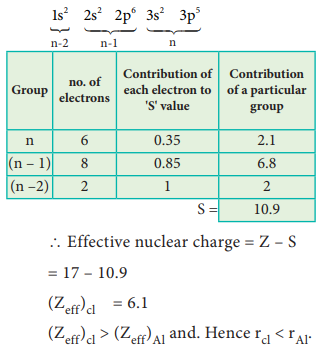
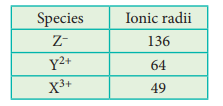
5. A student reported the ionic
radii of isoelectronic species X3+, Y2+ and Z-
as 136 pm, 64 pm and 49 pm respectively. Is that order correct? Comment.
Answers:
X3+, Y2+, Z–
are isoelectronic.
Effective nuclear
charge is in the order
(Zeff )Z- < (Zeff
)Y2 + < (Zeff
)X3+ and
Hence, ionic radii should be in
the order
rZ -
> rY2
+ > rX3+
The correct values are,
6. The first ionisation energy (IE1)
and second ionisation energy (IE2) of elements X, Y and Z are given
below.
Element : IE1
(kJ mol-1) : IE2 (kJ mol-1)
X : 2370 :
5250
Y
: 522 : 7298
Z : 1680 :
3381
Which one of the above elements is
the most reactive metal, the least reactive metal and a noble gas?
Answers:
Noble
gases : Ioniation energy ranging from 2372 KJmol–1 to 1037 kJ mol–1.
For element X, the IE1,
value is in the range of noble gas, moreover for this element both IE1
and IE 2 are higher and hence X is the noble gas.
For Y, the first ionisation energy is low and
second ionisation energy is very high and hence Y is most reactive metal.
For Z, both IE1 and IE2
are higher and hence it is least reactive.
7. The electron gain enthalpy of
chlorine is 348 kJ mol-1. How much energy in kJ is released when
17.5 g of chlorine is completely converted into Cl- ions in the
gaseous state?
Answers:
Cl(g) + e– → Cl–(g) ∆H = 348 kJ mol–1
For one mole (35.5g) 348 kJ is
released.
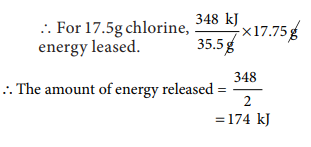
Related Topics