Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 3 : Periodic Classification of Elements
Electron gain enthalpy (Electron Affinity)
Electron Affinity
It is defined as the amount of energy released (required in the case noble gases) when an electron is added to the valence shell of an isolated neutral gaseous atom in its ground state to form its anion. It is expressed in kJ mol-1
A + 1 e- ‚Üí A- + EA
Variation of Electron Affinity in a period:
The variation of electron affinity is not as systematic as in the case of ionisation energy. As we move from alkali metals to halogens in a period, generally electron affinity increases, i.e. the amount of energy released will be more. This is due to an increase in the nuclear charge and decrease in size of the atoms. However, in case of elements such as beryllium (1s2, 2s2), nitrogen (1s 2, 2s 2, 2p3) the addition of extra electron will disturb their stable electronic configuration and they have almost zero electron affinity.
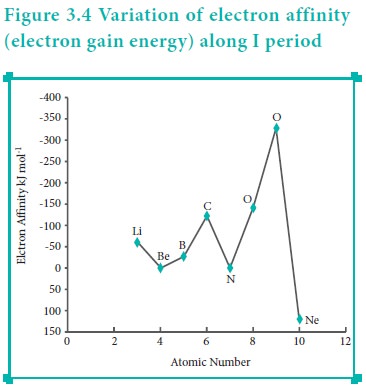
Noble gases have stable ns2, np6 configuration, and the addition of further electron is unfavourable and requires energy. Halogens having the general electronic configuration of ns2, np5 readily accept an electron to get the stable noble gas electronic configuration (ns2, np6), and therefore in each period the halogen has high electron affinity. (high negative values)
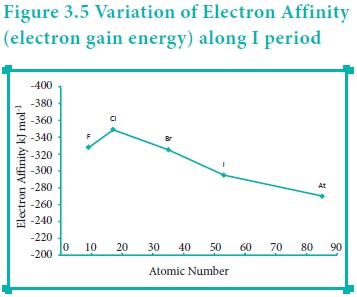
Variation of Electron affinity in a group:
As we move down a group, generally the electron affinity decreases. It is due to increase in atomic size and the shielding effect of inner shell electrons. However, oxygen and fluorine have lower affinity than sulphur and chlorine respectively. The sizes of oxygen and fluorine atoms are comparatively small and they have high electron density. Moreover, the extra electron added to oxygen and fluorine has to be accommodated in the 2p orbital which is relatively compact compared to the 3p orbital of sulphur and chlorine so, oxygen and fluorine have lower electron affinity than their respective group elements sulphur and chlorine.
Related Topics