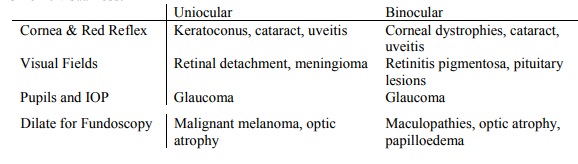
Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Neuro-sensory
Loss of Vision
Loss of Vision
·
Is it bilateral or unilateral?
·
Sudden: Woke up with it Ăž
Vascular: Central retinal artery or vein occlusion, ischaemic optic neuropathy,
vitreous haemorrhage, CVA, preretinal haemorrhage
·
Suddenish: Gradual over a few
days: Closed angle glaucoma (hours), infection, inflammation, retinal
detachment, optic neuritis
·
Gradual: Months to Years:
Refractive, cataract, primary open angle glaucoma, age related macular
degeneration, retinopathy (eg diabetes, hypertension)
·
Chronic visual loss:
Age Related Macular Degeneration
·
Loss of visual acuity with
peripheral vision in tact
·
Observe stippling and
depigmentation of macular
·
Can be uni or bilateral
·
Age-related types:
o Dry (atrophic) macular degeneration: thinning of macula, gradual. No
cure. Atrophy of photoreceptors, loss of outer nuclear layer
o Wet (exudative) macular degeneration: May be due to Choroidal
Neovascular Membranes, unilateral with onset over several weeks. Straight lines
appear wavy ® refer as laser treatment slows progression
·
Symptoms: blurred central vision,
distortion of straight lines
Eye Trauma
·
Mechanical: blunt/sharp,
superficial/penetrating
·
Chemical: alkali the worst. Local
anaesthetic then irrigate for 30 minutes (less time already irrigated before
presentation). If not toxic nor significantly inflamed, if VA OK and no
fluorescein staining then chloramphenicol eyedrops qid for 5 days
·
Radiation: UV, thermal, arch
flash. Comes on hours after exposure, is very painful. Eye is very red,
multiple fine specks of fluorescein staining. Usually resolves in 24 hours.
Treat as an abrasion (pad both eyes)
·
Hyphema: blood in anterior
chamber. Refer for opinion but don‟t normally treat. Check for corneal
abrasion, traumatic mydriasis, eye movements, blowout fracture of orbital
floor, intra-ocular bleed
·
Penetrating Eye Injuries can be
missed by subconjunctival bleed. Always refer if at risk. If metal vs. metal,
always do an xray otherwise blind from Fe toxicity. Also rose thorns. Teardrop
shaped cornea is a PEI until proven otherwise. Refer immediately. Lie down, im
antiemetic to prevent vomiting.
·
Keep nil-by-mouth
·
Distorted pupil: penetrating
injury until proven otherwise Ăž nil by mouth, shield eye, antibiotics, antiemetic, refer
·
Foreign bodies: remove with
25-gauge needle and topical anaesthetic drops. Steady fixation of eye is key.
Always evert upper key lid to look for further foreign bodies
·
Corneal abrasions: Very painful
and photophobic. Stain with fluorescein. Most heal within 24 hours. Refer if
abrasion large or central, if cornea hazy, VA reduced or eye is very inflamed.
Double pad eye well. Apply chloramphenicol ointment stat and bd for 5 days.
Never give anaesthetic drops to take home – can cause ulceration and blindness
·
Lid laceration: sow up anything
not penetrating, or not involving lid margin or tear drainage (refer these)
Retinal Detachment
·
Higher risk in near-sighted
(myopic)
·
Can be caused by blunt trauma
·
Due to vitreous shrinkage,
tears/holes in retina (eg with age), or underlying pathology
·
Symptoms: sudden changes in
vision – watery or shadowy patch, sudden  in number of floaters (spots in
vision), loss of visual field (like a descending curtain)
·
Need rapid treatment: seal tear
with laser
·
Causes:
o Exudative detachment: accumulation of fluid under the retina due to
leaky vessels, eg tumour, vascular abnormality
o Traction detachment: vitreous becomes organised following trauma or
neovascularisation and pulls on the retina
Related Topics