Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Cardiovascular
Heart sounds - Physical Exam
Heart sounds
·
Stethoscope head:
o Bell: good for low pitched sounds, eg diastolic murmur (mitral stenosis)
or 3rd heart sound. Don‟t press too hard otherwise skin becomes a diaphragm
o Diaphragm: good for high pitched sounds, eg systolic murmur or 4th heart sound
·
Using stethoscope, ausciltate:
o Mitral area (4th intercostal space, left mid-clavicular line) with bell and diaphragm
o Tricuspid area (5th intercostal space, left sternal edge) with diaphragm
o Pulmonary area (second intercostal space, left sternal edge) with
diaphragm
o Aortic area (second intercostal space, right sternal edge) with
diaphragm
·
Heart Sounds:
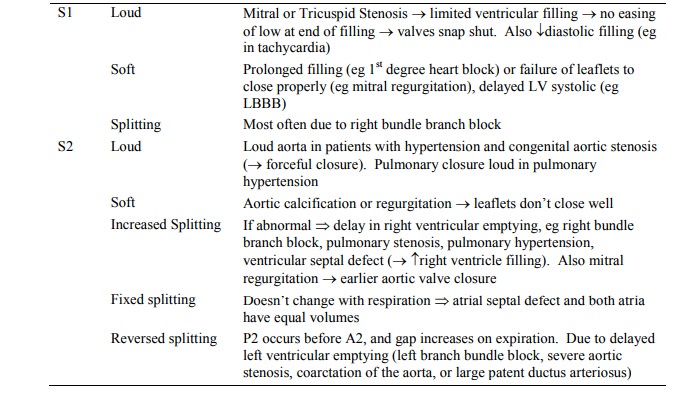
o First heart sound: closure of mitral and tricuspid valves at beginning
of systole. Mitral closes slightly before tricuspid but you won‟t hear the
difference
o Second heart sounds: closure of aortic and pulmonary valves. Lower
pitch. End of systole. Aortic closes first (higher back pressure on valve) ®
splitting of heart sounds. But pulmonary closure is not heard over all the
praecordium, so splitting best heard over pulmonary area. Inspiration ® venous
return ® later closure of pulmonary valve ® enhanced splitting
o Use carotid pulsation to orientate to timing. This occurs during systole, between S1 and S2
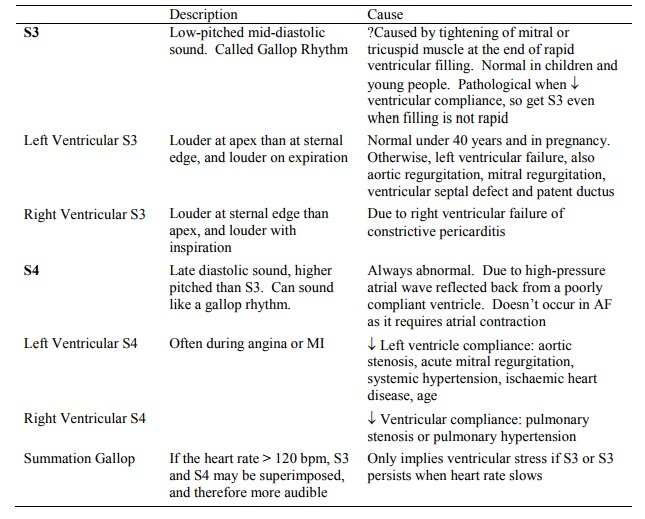
Abnormal Heart Sounds
Extra Heart Sounds
Miscellaneous Sounds
·
Opening Snap: High-pitched sound
after S2 in mitral stenosis, due to sudden opening of the mitral valve. Don‟t
confuse with widely split S2 (snap is higher pitched)
·
Systolic ejection click: early
systolic high-pitched sound over aortic or pulmonary areas. Is caused by
pulmonary or aortic congential stenosis and is followed by a systolic ejection
murmur
·
Non-ejection systolic click: high
pitched systolic sound over the mitral area. Common. May be followed by
systolic murmur. Due to mitral prolapse and atrial septal defects
·
Diastolic pericardial knock: may
occur if there is a sudden cessation of ventricular filling in constrictive
pericardial disease
Related Topics