Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Pharmacology
Cardiovascular Pharmacology
· For Anti-coagulation,see Anticoagulant Treatment Topic
Idiot’s guide
·
Always push non drug treatment:
lifestyle, smoking, etc
·
Hypertension: Thiazides (not
diabetics or gout) + b-blockers (not CORD/asthma). Maybe ACE inhibitors
·
Angina: b-blockers
+ aspirin + nitrates. Maybe Ca channel blockers (¯HR),
statins, ACE (if hypertension/diabetes)
·
Post MI: Aspirin, b-blockers,
ACE if ¯LVF +/- statin
·
Heart Failure: ACE + diuretic +
aspirin. Maybe b-blockers, spironolactone, other vasodilators, statins, etc
ACE Inhibitors
·
Block the formation of
angiotensin II ® diuretic, ¯peripheral vascular resistance, and better tissue remodelling/healing of
damaged myocardium. But 30% of hypertensives are non-responders
·
Eg Captopril, quinapril
·
Many patients (especially the
elderly) don‟t respond on its own. Synergistic effect with diuretic (ie shifts
ACE inhibitor dose-response curve to the left). If it‟s not working, add in a
low dose diuretic
·
Adverse effects:
o Metabolic taste, hypotension (especially with first few doses), hyperkalaemia,
angioedema, neutropenia, proteinuria.
o ¯Renal
function, especially if existing renal impairment (efferent
flow ® ¯glomerular filtration)
o Dry cough (due to bradykinins). If cough a problem, then use an angiotensin II receptor
antagonist (eg Losartan)
o Rash: may be long time after starting, especially captopril due to
sulphur group
·
Interactions:
o Diuretics: hypotension + ¯renal function
o NSAIDS: renal failure, hyperkalaemia
·
Contra-indications:
o Bilateral renal artery stenosis
o Pregnancy, breast feeding
o LV outflow obstruction (eg Aortic Stenosis)
o Marked hypotension
o Other drugs: K supplements, Li, NSAIDs
·
Monitor for: ¯Na, K, Cr
> 200, rare neutropenia
Diuretics
·
Common types:
o Thiazides eg bendrofluazide. Flat dose response curve so dose only
side effects. No effect from a dose above 2.5 mg. Effect: mainly vasodilation, also
inhibit Na/K co-transport in distal convoluted tubule ® salt and
water loss. VERY cheap. Take 6 – 8 weeks to work
o Frusemide: blocks Na/K/Cl transport in Loop of Henle. No role in lowering blood pressure
·
Interactions:
o General: NSAIDs, lithium, digoxin, ACE inhibitors, corticosteroids
o Loop: antibiotics
o Thiazides: calcium supplements
·
Adverse drug reactions are dose
dependent (Þ use in low dose):
o General: dehydration, electrolytes, lipids, endocrine, skin
o Loop: ototoxicity, ¯K, ¯Ca. Frusemide ® water
rush. Difficult if you‟re out and about ®
o ¯compliance
o Thiazide:¯K, Ca, ¯Mg, urate (+/- gout), lipids, progressive glucose rise over years, thrombocytopenia, impotence
in high doses
·
Spironolactone:
o Acts at distal renal tubule as an aldosterone antagonist
o Adverse effects: hyperkalaemia, diarrhoea, gynaecomastia
o Interactions: ACE inhibitors, digoxin
b-blockers
·
Action (effect takes 2 – 4
weeks):
o Renal effect (¯renin)
o Pre-synaptic b-receptor blocker
o ¯Cardiac
output due to ¯rate and strength of myocardial contraction (® ¯O2
consumption). Acutely ® TPR (so not if peripheral vascular disease otherwise ischaemia).
¯CO resolves over time
o ?Central action
·
Use in angina, hypertension,
heart failure
·
Classified by:
o Lipid vs H2O soluble
o b-receptor
selectivity
o a-blocking
activity (eg labetalol ® prone to postural hypotension)
·
Contraindications:
o Arrhythmias: bradycardia and AV block
o Asthma
o Peripheral vascular disease: lead to unopposed a1 stimulation
o Diabetes: block the symptoms of hypoglycaemia, potentiate effects of
insulin and oral hypoglycaemics
o Overt cardiac failure: negative inotropes – but still OK in heart
failure at low dose
·
Adverse effects (generally dose
dependent):
o Common: Lethargy, heavy legs (slowed up feeling due to ¯CO), cold
extremities, lipids, headaches, nightmares (in lipid soluble propranolol, not water
soluble atenolol)
o Less common: GI disturbances and rashes
o Rapid withdrawal ® angina, arrhythmias due to b1 up-regulation
·
Interactions with:
o Verapamil: severe bradycardia
o Cimitidine: inhibits metabolism ® potentiates effect
·
Consider a-blockers
for hypertension– but not as first line agents (may exacerbate heart failure).
Dilate peripheral arterioles (modern ones don‟t cause reflex tachycardia), less
arterial dilation. Start low to avoid profound hypotension (especially
elderly). Good for lipids
Ca Channel Blockers
·
Uses: Angina, dysrhythmias,
hypertension, NOT heart failure
·
Hypertension: only in isolated
systolic hypertension (eg due to hardened arteries)
·
Not better than diuretics or b-blockers
for hypertension, but additive effect
·
Action: ¯myocardial
work, decrease afterload, vasodilate coronary arteries
o Verapamil (originally an anti-arrhythmic, derivative of theophylline, less effect on vasodilation but bradycardia) and Diltiazem: slow conduction at the AV node and cause coronary vasodilation
o Nifedipine: vasodilator Þ good for coronary artery spasm, but may also cause reflex tachycardia
so may use with a b-blocker
·
Adverse effects:
o All cause headache, flushing, dizziness, hypotension, ¯LV
function
o Verapamil: constipation
o Verapamil and diltiazem: heart block
o Nifedipine and verapamil: blood sugar
·
Interactions:
o plasma
digoxin levels
o Enzyme inhibitors ® plasma levels of carbamazepine and cyclosporin
o Don‟t use verapamil with b-blockers: bradycardia + LVF
·
Also consider long acting
nitrates
Positive Inotropes
·
Digoxin: only oral inotrope. Slows AV conduction and increases
contractility
o Use: in AF, slows rate ® output. But poor for rate control
– still HR in response to standing up
o Orally takes a week to reach steady state (T½ is 36 – 40 hours)
o Shortens QT interval ® causes digitalis effect on ST interval (not a sign of toxicity)
o Low therapeutic index (although wide therapeutic range) ® toxicity
common:
§ CV: any arrhythmia, arrest,
worsening heart failure
§ GI: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pain
§ CNS: headache, drowsiness, unsteadiness, blurred/yellow vision, confusion
§ Worse if:
·
Electrolyte disturbance:
hypokalaemic, hypercalcaemia, alkalosis
·
Potassium sparing diuretics,
steroids, verapamil, amiodarone, spironolactone
·
Disease: hypothyroidism, hypoxia,
renal failure
·
Old age
§ Management: stop digoxin, check plasma level and K, treat arrhythmias,
antidote (Digibind)
·
Dopamine (precursor of
nor-adrenaline)
o In low doses ® renal vasodilation and improved renal function
o In higher doses ® acts on cardiac b1 receptors ® inotropic effects
·
Dobutamine: acts on cardiac b1
receptors ® inotropic effects
Lipid Lowering Drugs
· See Dyslipidaemia(Topic)
·
Lipids:
o Cholesterol is most concentrated in LDL
o HDL is beneficial
o VLDL carries TAGs
·
Hypercholesterolaemia:
o Primary: Hepatic overproduction of VLDL ® VLDL/LDL/Remnant
lipoproteins
o Secondary: Obesity, diabetes, hypothyroidism, nephrotic syndrome,
alcohol, drugs (oestrogen, Retinoids, b-blockers, thiazides….)
·
Drug groups:
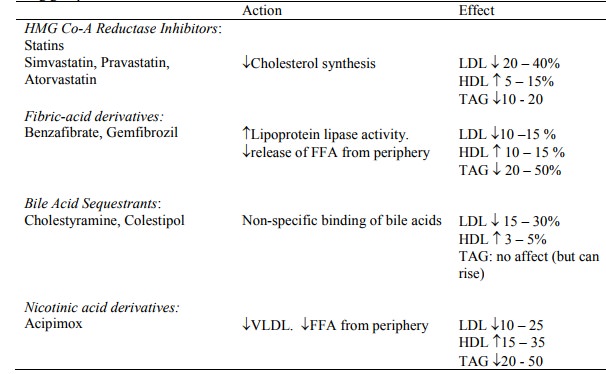
·
HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
(Statins):
o Treatment: Requires health benefits approval (it‟s expensive) and is
always accompanied by diet
o More effect in lowering plasma concentrations of LDL and total
cholesterol ® ¯mortality in hypercholesterolaemia + angina
o SE: rare. GI, headaches, LFTs,
myopathy from Ck. Potentiates warfarin
·
Fibrates: HDL and ¯TAGs
·
Bile-acid sequestrants: Indicated
for children and women of childbearing age. SE: constipation, skin rashes. Bind
fat soluble vitamins and other drugs (eg warfarin, give two hours before or 4
hours after)
Related Topics