Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 8 : Physical and Chemical Equilibrium
Equilibrium constants for heterogeneous equilibrium
Equilibrium constants for heterogeneous equilibrium
Consider the following heterogeneous equilibrium.
CaCO3 (s) ⇌ CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
The equilibrium constant for the above reaction can be written as
Kc = [CaO(s)][CO2(g)] / CaCO3 (s)
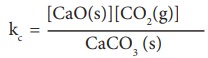
A pure solid always has the same concentration at a given temperature, as it does not expand to fill its container. i.e. it has same number of moles L-1 of its volume. Therefore, the concentration of a pure solid is a constant. The above expression can be modified as follows
Kc = [CO2 (g)]
Or
Kp = pCO2
The equilibrium constant for the above reaction depends only the concentration of carbon dioxide and not the calcium carbonate or calcium oxide. Similarly, the active mass (concentration) of the pure liquid does not change at a given temperature. Consequently, the concentration terms of pure liquids can also be excluded from the expression of the equilibrium constant.
For example,
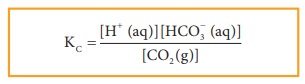
CO2(g) + H2O (l) ⇌ H+(aq) + HCO3– (aq)
Since, H2O (l) is a pure liquid the Kc can be expressed as
Example
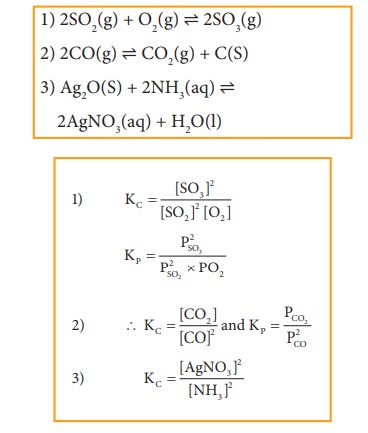
Write the Kp and Kc for the following reactions
Related Topics