Chapter: Biology of Disease: Disorders of the Blood
Disorders of the Blood
DISORDERS OF THE BLOOD
INTRODUCTION
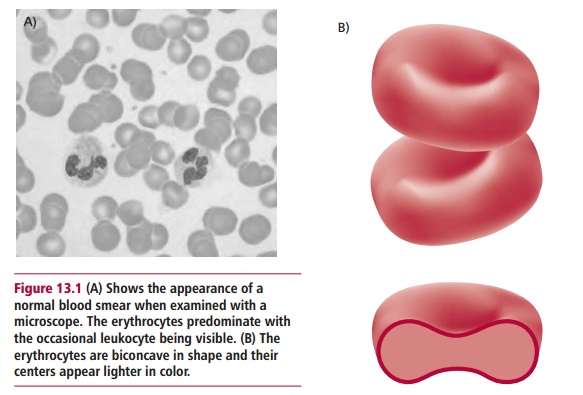
Blood is a protein-rich fluid called plasma in which erythrocytes and
leukocytes, sometimes called red and white blood cells respectively, and
platelets are suspended (Figure 13.1).
The cells constitute about 40–45% of the volume of the blood. The blood is
pumped around the body by the heart through the arteries that supply the
capillaries and is returned to the heart in the veins . The main functions of
the blood are to distribute oxygen, nutrients and hormones and other signaling
molecules between tissues and to remove carbon dioxide and other waste
products. Plasma contains the proteins of the clotting system and of the immune
systems.
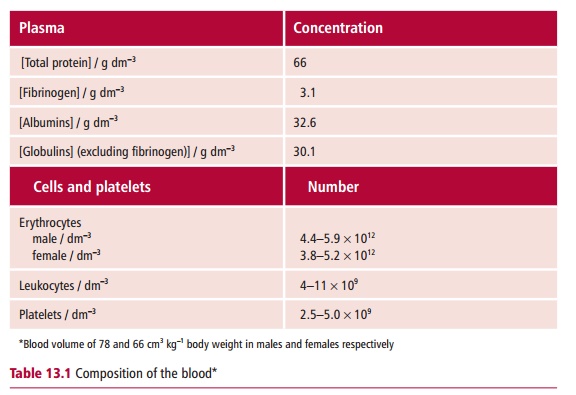
Plasma is blood from which the cells have been
removed. It contains a range of plasma proteins in addition to the clotting and
immune system proteins mentioned above, nutrients, such as glucose, waste
materials, for example urea, and a range of electrolytes in solution. If it is
allowed to clot, the clear straw-colored liquid remaining after removal of the
clot is called serum. The
composition of the blood and the plasma is given in Table 13.1.
In a text of this size it is not, of course, possible
to discuss each type of blood disorder and attention will focus only on the
major types of diseases likely to be normally encountered.
Related Topics