Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Covalent bond: Lewis dot structure and Double bond formation
Covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond formed when two atoms mutually share a pair of electron. By doing so, the atoms attain stable octet electronic configuration. In covalent bonding, overlapping of the atomic orbitals having an electron from each of the two atoms of the bond takes place resulting in equal sharing of the pair of electrons. Also the interatomic bond thus formed due to the overlap of atomic orbitals of electrons is known as a covalent bond. Generally the orbitals of the electrons in the valency shell of the atoms are used for electron sharing. The shared pair of electrons lie in the middle of the covalent bond. Including the shared pair of electrons the atoms of the covalent bond attain the stable octet configuration. Thus in hydrogen molecule (H2) a covalent bond results by the overlap of the two s orbitals each containing an electron from each of the two H atoms of the molecule. Each H atom attains '1s2 ' filled K shell.
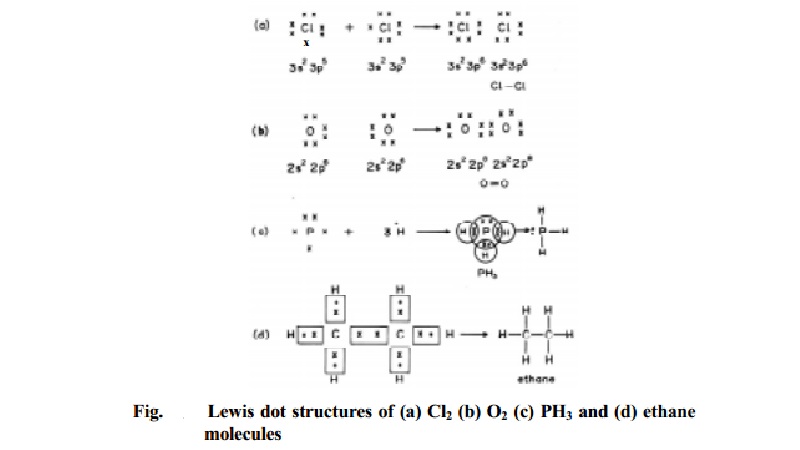
A covalent bond can be formed by sharing of s,p,d,f electrons also. Consider Cl2 molecule. The outer shell electronic configuration of atom is 3s2 2px2 2py2 2pz1. When each chlorine atom mutually share the 2pz unpaired electron contributed from each Cl atom of the molecule, a covalent bond is formed. By doing so, each chlorine atom attains argon electron configuration.
The Lewis dot structure will be :
More than one e- can also be mutually shared to result in two covalent bonds between the atoms of a bond. Example in O2 molecule (O=O) 2 covalent bonds exist.
The two unpaired electrons in 2py and 2pz orbitals of each of O atom is mutually shared so that after the double bond formation stable octet electronic configuration is attained by each oxygen atom of the molecule.
In the phosphine PH3 molecule, three hydrogen atoms combine with one phosphorous atom. Each hydrogen atom shares its 1s electron with phosphorous. So that three covalent bonds are formed in PH3. The lewis dot structure is in Fig.
In case of ethane molecule, the six C-H bonds and a C-C bond are covalent in nature. They are formed by mutual sharing of a pair of electrons between the two atoms of a bond. Each carbon atom completes its stable octet and each H atom has completed K shell.

Double bond formation
In oxygen (O2) molecule, two pairs of electrons are mutually shared and a double bond results. The electronic configuration of O atom is 1s2 2s2 2p4. By sharing two more electrons from the other O atom, each O atom attains 2s2 2p6, filled configuration. Thus O2 molecule is represented as O = O. Similar to oxygen molecule in ethylene which is an organic molecule, a double covalent bond exists between the two carbon atoms due to the mutual sharing of two pairs of electrons. Each carbon atom attains the stable octet electron configuration.
Related Topics