Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Causes for deviation of real gas from ideal behaviour
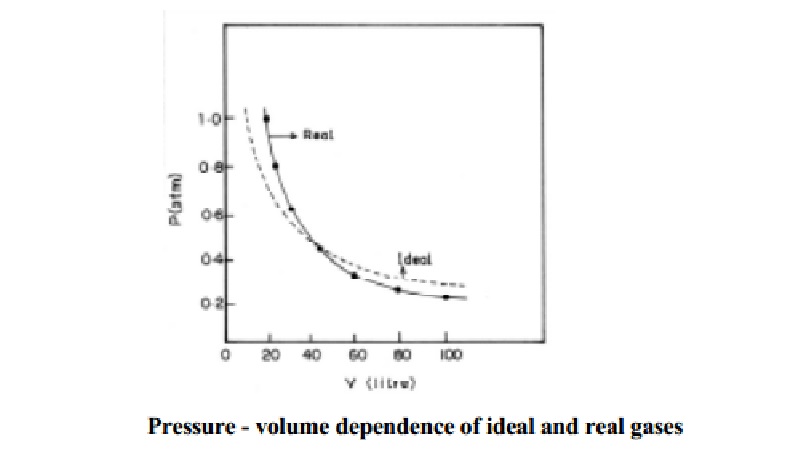
Causes for deviation of real gas from ideal
behaviour
The
perfect gas equation of state is given by
PV = nRT
The gases which obey this equation exactly are referred as ideal gases
or perfect gases. Real gases do not obey the perfect gas equation exactly. Real
gases show deviation because of intermolecular interaction of the gaseous
molecules. Repulsive forces between the molecules cause expansion, and
attractive forces cause reduction in volume. Under the conditions of low
pressure and high temperature the inter-molecular interactions of the gaseous
molecules are lower and tend to behave ideally under these conditions. At other
conditions of pressure and volume, deviations are seen.
Volume deviation
Based on
one of the postulates of the kinetic theory of the gases it is assumed that the
volume occupied by the gaseous molecules themselves is negligibly small
compared to the total volume of the gas. This postulate holds good for ideal
gases and only under normal conditions of temperature and pressure for real
gases. When temperature is lowered considerably, the total volume of the real
gas decreases tremendously and becomes comparable with the actual volume of
gaseous molecules. In such cases, the volume occupied by the gaseous molecules
cannot be neglected in comparison with total volume of the gas.
Thus, the volume deviations created at high
pressure and low temperature make the real gas to deviate from the ideal
behaviour.
Pressure deviation
For an ideal gas the forces of attraction
between the gaseous molecule are considered to be nil at all temperature and
pressure.
For a real gas this assumption is valid only at
low pressure or at high temperature. Under these conditions, the volume of the
gas is high and the molecules lie far apart from one another. Therefore the
intermolecular forces of attraction becomes negligible.
But at
high pressure (or) at low temperature, the volume of the gas is small and
molecules lie closer to one another. The intermolecular forces of attraction
becomes appreciable and cannot be neglected. Therefore it is necessary to apply
suitable corrections to the pressure of the real gas in the equation of state.
Related Topics