Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Alkali Metals: General characteristics, Physical Properties
Alkali Metals
Position of alkali
metals in the periodic table
Alkali metals occupy the group I of the periodic
table. Elements lithium, sodium, potassium, rubiduim, caesium and francium
constitute alkali metals. They are named so from the Arabic word `Alquili'
meaning `plant ashes'. Ashes of plants are composed mainly of sodium and
potassium carbonates.
General
characteristics
1.
The alkali metals are shiny white and soft.
2.
They can be readily cut with a knife.
3.
They are extremely reactive metals and form
strong alkaline oxides and hydroxides.
4.
The last metal of this group, francium is
radioactive.
5.
Since the alkali metals are extremely reactive
they occur only as compounds in nature.
6.
All the alkali metals exhibit an oxidation state
of +1. This is because the metals can easily lose their single outermost
electron.
7.
The alkali metals give characteristic colour in
bunsen flame. The colours given by Li, Na and K are crimson red, yellow, lilac
respectively. This is because when the alkali metal or any of its compounds are
heated in a bunsen flame, the ns' electron gets excited to higher energy levels
and while returning to their ground state the excitation energy absorbed by
them is released as light in the visible region.
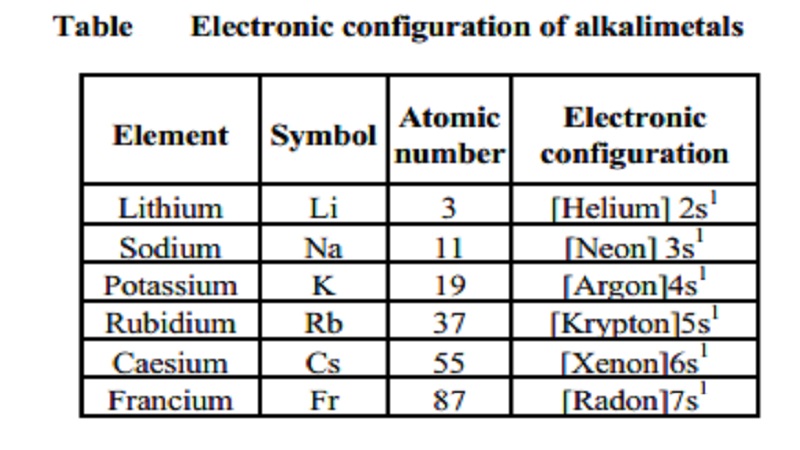
Table Electronic configuration of alkalimetals
Element Symbol Atomic Electronic
number configuration
Lithium Li 3 [Helium]
2s1
Sodium Na 11 [Neon]
3s1
Potassium K 19 [Argon]4s1
Rubidium Rb 37 [Krypton]5s1
Caesium Cs 55 [Xenon]6s1
Francium Fr 87 [Radon]7s1
Gradation in Physical Properties
1.
Density: In general, these elements have high density due
to the close packing of atoms in
their metallic crystals. Lithium has low density due to the low atomic weight
of the atom. Density of the elements increases on moving down the group due to
the increase in the mass of the atoms with increasing atomic number. However, K
is lighter than Na probably due to an unusual increase in atomic size.
2.
Atomic volume: Atomic volume
increases on moving down the group
from Li to Cs. Hence there is an increase in atomic and ionic radii in the same
order.
3.
Melting and boiling points : All alkali
metals have low melting and boiling
point due to the weak bonding in the crystal lattice. The weak interatomic
bonds are attributed to their large atonic radii and to the presence of one
valence electron. With the increase in the size of the metal atoms, the
repulsion of the non-bonding electron gets increased and therefore melting and
boiling points decreases on moving down the group from Li to Cs.
4.
Ionization energy : The first ionization
energies of alkali metals are relatively
low and decreases on moving down from Li to Cs.
i.
M(g) -- > M+(g) + 1e-
As the atomic
radius gets increased on moving down the group, the outer electron gets farther
and farther away from the nucleus and therefore ionization energy decreases.
The second
ionization energies of alkali metals are fairly high. This implies that the
loss of the second electron is quite difficult, because it has to be pulled out
from the noble gas core.
5.
Electropositive character : As alkali
metals have low ionization energies,
they have a great tendency to lose electrons forming unipositive ions. Therefore
they
M -- > M+ + 1e-
have
strong electropositive character. Electropositive character increases as we go
down the group. The alkali metals are so highly electropositive that they emit
electrons when irradiated with light. This effect is known as photoelectric
effect. Due to this property, Cs and K are used in photoelectric cells.
6.
Oxidation state: All the alkali metals
have only one electron in their
outermost valence shall. As the penultimate shell being complete, these
elements lose one electron to get the stable configuration of the nearest inert
gas. Thus, they are monovalent elements showing an oxidation state of +1.
7.
Reducing properties : As alkali
metals have low ionization energy, they
lose their valence electrons readily and thus bring about reduction reaction.
Therefore these elements behave as good reducing agents.
Related Topics