Chapter: Orthopaedics
Humeral Fracture
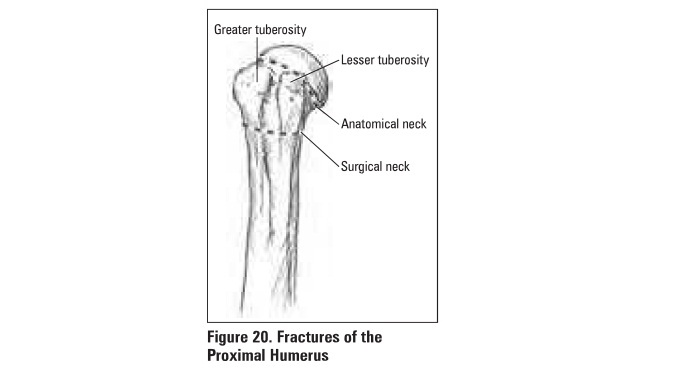
Humerus
Proximal Humeral Fracture
Mechanism
·
young: high energy trauma (MVA)
·
older: FOOSH from standing height in osteoporotic
.individuals
Clinical Futures
·
pain, swelling, tenderness, painful ROM
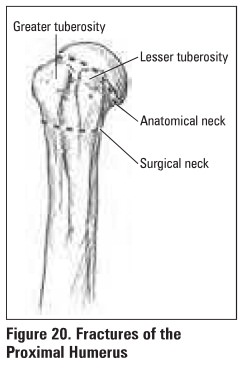
Investigations
·
test a:xillary nerve function (deltoid function
and skin over deltoid)
·
x-rays: AP, trans-scapular, uiliary are essential
·
CT scan: to evaluate for articular involvement and
fracture displacement
Classification
·
Neer classification is based on 4 fracture
fragments: head, greater tuberosity, lesser tuberosity, shaft
• nondisplaced: displacement <1 cm and/or
angulation <45°
• displaced: displacement >1 cm and/or
angulation >45°
• dlslocated/subluxed: humeral head
dislocated/subbluxed from glenoid
Treatment
·
non-operative
• sling immobilization (nondlsplaced): begin
ROM in 7-10 days to prevent stiffness
• closed reduction (minimally displaced)
·
operative
• ORIF (anatomic neck fractures, displaced. dislocated)
• hemiarthroplasty may be necessary,
especially in elderly
Specific Complications (see
General Fracture Complications)
·
AVN, axillary nerve palsy, malunion,
post-traumatic arthritis
Humeral Shaft Fracture
Mechanism
·
direct blows/MVA (most common), FOOSH, twisting
injuries, metastases (in elderly)
Clinical Features
·
pain, swelling,± shortening. mot:lon/aepitus at
fracture site
·
must test ra.d1al. nerve function before and after
treatment
Investigations
·
x-rays: AP and lateral radiographs of the humerus
including the shoulder and elbow joints
Treatment
·
in general. humeral shaft fractures are t:n:ab:d
non-operatively
·
non-operative (most common)
o
± reduction- am accept deformity due to
compensatory range of motion of shoulder
o
hanging cast (weight of arm in cast provide&
traction across fracture site) with sling immobilization x 7-10 days, then
Sarmiento functional brace
·
operative
o
indications: open fracture, neurovascular injury,
unacceptable fracture alignment, polytrauma. segmental fracture. pathological
fracture, "floating elbow" (simultaneous unstable humeral and furearm
fractures), intra-articular
o
procedure: compression plating (most common),
Intramedullary rod Insertion, external fixation
Specific Complications (see
General Fracture Complications)
·
radial nerve Injury: expect spontaneous recovery
in 3-4 months, otherwise send for electromyography (BMG)
·
decreased ROM
·
compartment syndrome
Related Topics