Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Determination of Molecular Mass Victor-Meyer's Method
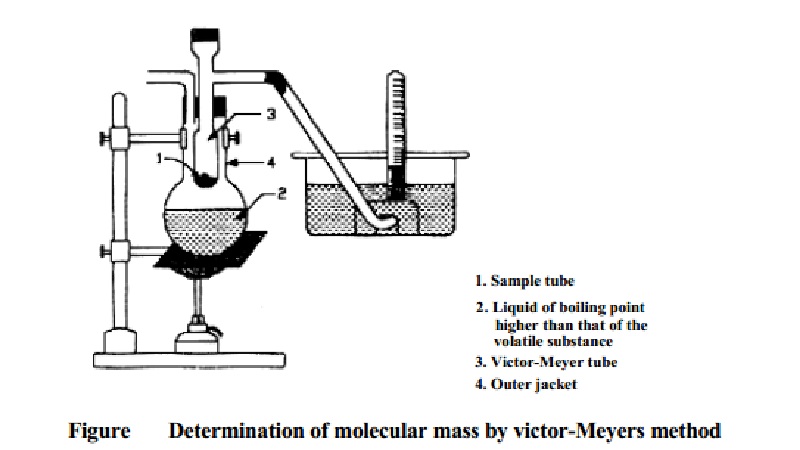
Determination of
Molecular Mass Victor-Meyer's Method
Principle
In this
method a known mass of a volatile liquid or solid is converted into its vapour
by heating in a Victor-Meyer's tube. The vapour displaces its own volume of
air. The volume of air displaced by the vapour is measured at the experimental
temperature and pressure. The volume of the vapour at s.t.p is then calculated.
From this the mass of 2.24 x 10-2m3 of the vapour at
S.T.P. is calculated. This value represents the molecular mass of the
substance.
method
The apparatus consists of an inner Victor-Meyer tube, the lower end of
which is in the form of a bulb. The upper end of the tube has a side tube which
leads to a trough of water. The Victor-Meyer tube is surrounded by an outer
jacket. In the outer jacket is placed a liquid which boils at a temperature at
least 30 K higher than the boiling point of the volatile substance under study.
A small quantity of glass wool or asbestos fiber covers the bottom of the
Victor-Meyer tube to prevent breakage when the bottle containing the substance
is dropped in.
Procedure
The liquid in the outer jacket is allowed to boil and when no more air
escapes from the side tube, a graduated tube filled with water is inverted over
the side tube dipping in a trough full of water. A small quantity of the
substance is exactly weighed in a small stoppered bottle and quickly dropped in
the heated Victor-Meyer tube and corked immediately.
The bottle
falls on the asbestos pad and its content suddenly changes into vapour, blow
out the stopper and displace an equal volume of air which collects in the
graduated tube. The volume of air in the graduated tube is measured by taking
it out by closing its mouth with the thumb and dipping it in a jar full of water.
When the water levels outside and inside the tube are the same, the volume of
air displaced is noted. The atmospheric pressure and laboratory temperature are
noted.
Calculations
Mass of
the volatile substance = wg
Volume of
air displaced = Volume of vapour = V1 m3
Laboratory
temperature = T1 K
Let the atomospheric pressure be P
Pressure of dry vapour = Atomospheric pressure - aqueous tension at. T1
K Let the aqueous tension be p Nm-2 at that temperature.
Pressure
of dry vapour = P1 = [P-p]
Standard
temperature = T0 = 273 K
Standard
pressure = = P0 = = 1.013 x 105 Nm-2
Let the volume of the vapour at standard temperature and pressure be V0
m3
From the
gas equation, it follows
P0V0 / T0
= P1 V1 / T1
V0 = (P1 V1
/ T1) x (T0/ P0)
The mass of V0 m3 of vapour at s.t.p is w g.
The mass
of 2.24 x 10-2 m3 of the vapour at s.t.p. is
= 2.24x10-2xW
/ V0
The value thus calculatd gives the molecular mass
Molecular mass
= 2 x vapour
density
Vapour
density = Molecular mass / 2
Related Topics