Chapter: 11 th 12th std standard Bio Botany plant tree Biology Higher secondary school College Notes
Xerophytes and Classification of Xerophytes
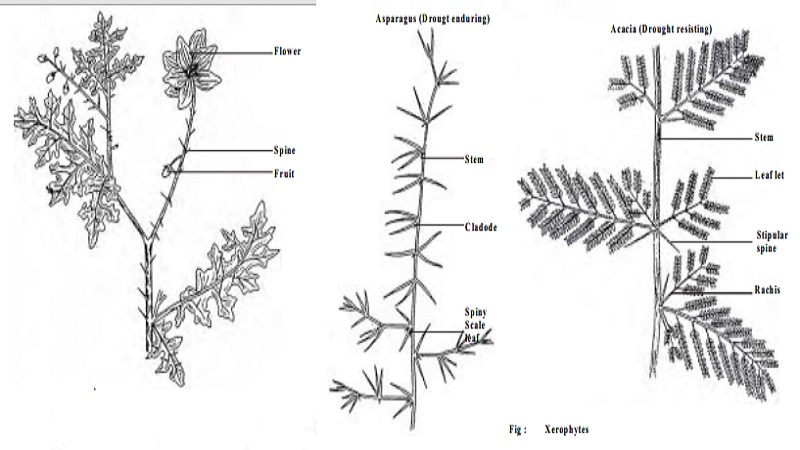
Xerophytes
Plants, which grow in dry habitats or xeric conditions, are called xerophytes. Places where available water is not present in adequate quantity are termed xeric habitats, which may be of three types.
1. Physically dry habitats
Where water retaining capacity of the soil is very low and the climate is dry e.g. Desert, Rock surface etc.
2. Physiologically dry habitats
Places where water is present in excess amount, but it is not absorbed by the plants easily.
3. Physically and physiologically dry habits e.g. Slopes of mountains.
Daubenmire (1959) defined xerophytes as "plants which grow on substrate that usually become depleted of water to a depth of at least two decimeters during normal growth season."
Xeric habitats are characterized by
1. High temperature of atmosphere and soil
2. Deficiency of water and minerals
3. Presence of water deep in the soil.
4. High intensity of light
On the basis of morphology, physiology and life cycle patterns, xerophytes are classified into three categories.
1. Drought escaping plants
They are also called as Drought evaders. They are mostly found in arid zones. They are annuals, which complete their life cycles within a very short period of 6-8 weeks and thus escape dryness (e.g. ) Solanum xanthocarpum,
Argemone mexicana, Cassia tora etc.
2. Drought Enduring Xerophytes (Succulents)
These plants suffer from dryness in their external environment only. Their succulent, fleshy organs (stems, leaves, roots) serve as water storage organs which accumulate large amount of water during the brief raining reason. e.g Agave, Aloe, Euphorbia, Opuntia, Asparagus.
Fleshy Xerophytes
In some plants, stem becomes succulent which are called the 'Fleshy Xerophytes' as in Opuntia and Euphorbia.
Opuntia dilleni
It is a wild spiny shrub of a rid places. The flattenned, green stem segments called phylloclades are thick and fleshy and carry out the function of photosynthesis. The phylloclades contain lot of mucilage, which help in retaining water for long a item.
In plants like Opuntia dilleni, stems are flat without leaves and perform photosynthesis.
3. Drought resisting plants (Non- succulent perennial)
The drought resisting plants are the true xerophytes. They possess a number of morphological, anatomical and physiological characteristics, which enable them to withstand critical dry condition. Thus they suffer from dryness both in their internal as well as external environments. e.g Calotropis procera, Acacia nilotica, Zizyphus jujuba, Capparis aphylla, Casuarina, Nerium, Saccharumetc.
Related Topics