Chapter: Mechanical : Robotics : Robot Drive Systems and End Effectors
Working of a stepper motor
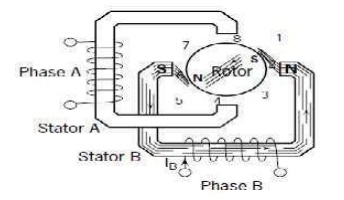
Working of a stepper motor
A stepper motor is an electromechanical device which
converts electrical pulses into discrete mechanical movements.
The shaft or spindle of
a stepper motor rotates in discrete step increments when electrical command
pulses are applied to it in the proper sequence. The motors rotation has
several direct relationships to these applied input pulses. The sequence of the
applied pulses is directly related to the direction of motor shafts rotation.
The speed of the motor shafts rotation is directly related to the frequency of
the input pulses and the length of rotation is directly related to the number
of input pulses applied.
This means that a
digital signal is used to drive the motor and every time it receives a digital
pulse it rotates a specific number of degrees in rotation.
Each step of rotation
is the response of the motor to an input pulse (or digital command). Step-wise
rotation of the rotor can be synchronized with pulses in a command-pulse train,
assuming that no steps are missed, thereby making the motor respond faithfully
to the pulse signal in an open-loop manner.
Stepper motors have
emerged as cost-effective alternatives for DC servomotors in high-speed,
motion-control applications (except the high torque-speed range) with the
improvements in permanent magnets and the incorporation of solid-state
circuitry and logic devices in their drive systems.
Today stepper motors
can be found in computer peripherals, machine tools, medical equipment,
automotive devices, and small business machines, to name a few applications.
Advantages of Stepper Motors:
Position error is noncumulative. A high
accuracy of motion is possible, even under open-loop control.
Large savings in sensor (measurement system)
and controller costs are possible when the open- loop mode is used.
Because of the incremental nature of command
and motion, stepper motors are easily adaptable to digital control
applications.
No serious stability problems exist, even
under open-loop control.
Torque capacity and power requirements can be
optimized and the response can be controlled by electronic switching.
Related Topics