Chapter: Mechanical : Robotics : Robot Drive Systems and End Effectors
AC Servo Motor | Stepper Motor

AC Servo Motor | Stepper Motor

Servos are controlled by
sending an electrical pulse of variable width, or pulse width modulation (PWM),
through the control wire. There is a minimum pulse, a maximum pulse and a
repetition rate. A servo motor can usually only turn 90° in either direction
for a total of 180° movement. The motor's neutral position is defined as the
position where the servo has the same amount of potential rotation in the both
the clockwise or counter-clockwise direction. The PWM sent to the motor determines position of the shaft, and
based on the duration of the pulse
sent via the
control wire the rotor will turn to the desired position. The
servo motor expects to see a pulse every 20
milliseconds (ms) and the length of the pulse will
determine how far
the motor turns.
For example, a 1.5ms pulse will
make the motor turn to
the 90° position.
Shorter than 1.5ms
moves it to 0° and any
longer than 1.5ms will turn the servo to 180°, as diagramed below.

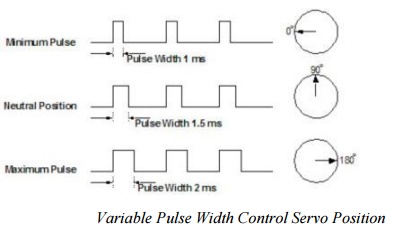
Variable Pulse Width
Control Servo Position
of a servo motor (L) and
an assembled servo (R)
When these servos are
commanded to move, they will move to the position and hold that position. If an
external force pushes against the servo while the servo is holding a position,
the servo will resist from moving out of that position. The maximum amount of
force the servo can exert is called the torque rating of the servo. Servos will
not hold their position forever though; the position pulse must be repeated to
instruct the servo to stay in position.
Related Topics