Chapter: Introduction to Human Nutrition: The Vitamins
Vitamers and niacin equivalents
Vitamers and niacin equivalents
Two compounds, nicotinic acid and nicotinamide, have the biological activity of niacin. When nicotinic acid was discovered as the curative and preventive factor for pellagra, it was already known as a chemical compound, and was therefore never assigned a number among the B vitamins. The name niacin was coined in the USA when it was decided to enrich maize meal with the vitamin to prevent pellagra; it was considered that the name nicotinic acid was not desirable because of its similarity to nicotine. In the USA the term niacin is commonly used to mean spe-cifically nicotinic acid, and nicotinamide is known as niacinamide; elsewhere “niacin” is used as a generic descriptor for both vitamers. Figure 8.10 shows the structures of nicotinic acid and niacin, as well as the nicotinamide nucleotide coenzymes, NAD and NADP.
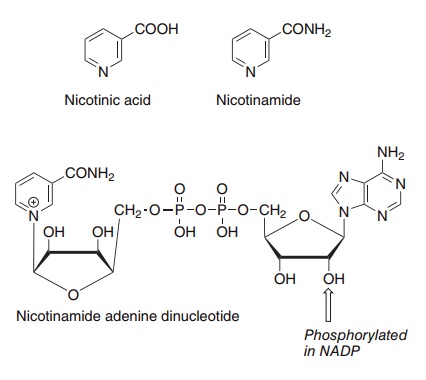
Figure 8.10 The niacin vitamers, nicotinic acid and nicotinamide, and the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
The nicotinamide ring of NAD can be synthesized in the body from the essential amino acid tryptophan. In adults almost all of the dietary intake of trypto-phan, apart from the small amount that is used for net new protein synthesis, and synthesis of the neu-rotransmitter serotonin, is metabolized by this pathway, and hence is potentially available for NAD synthesis.
Several studies have investigated the equivalence of dietary tryptophan and preformed niacin as precur-sors of the nicotinamide nucleotides, generally by determining the excretion of niacin metabolites in response to test doses of the precursors, in subjects maintained on deficient diets. The most extensive such study was that of Horwitt et al. in 1956. They found that there was a considerable variation between subjects in the response to tryptophan and niacin, and in order to allow for this individual variation they proposed the ratio of 60 mg of tryptophan equivalent to 1 mg of preformed niacin. Changes in hormonal status may result in considerable changes in this ratio, with between 7 and 30 mg of dietary tryptophan being equivalent to 1 mg of preformed niacin in late pregnancy.
The niacin content of foods is generally expressed as mg niacin equivalents; 1 mg niacin equivalent = mg preformed niacin + 1/60 × mg tryptophan. Because most of the niacin in cereals is biologically unavailable , it is conventional to ignore pre-formed niacin in cereal products.
Because endogenous synthesis from tryptophan is more important than preformed dietary niacin, the main dietary sources of niacin are generally those that are also rich sources of protein. It is only when the dietary staple is a cereal such as maize, which is remarkably lacking in tryptophan, that problems of deficiency occur. Trigonelline in coffee beans is demethylated to nicotinic acid during roasting, and moderate coffee consumption may meet a significant proportion of niacin requirements.
Unavailable niacin in cereals
Chemical analysis reveals niacin in cereals (largely in the bran), but this is biologically unavailable, since it is bound as niacytin – nicotinoyl esters to a variety of macromolecules. In wheat bran some 60% is esteri-fied to polysaccharides, and the remainder to poly-peptides and glycopeptides.
Treatment of cereals with alkali (e.g., by soaking overnight in calcium hydroxide solution, as is the tra-ditional method for the preparation of tortillas in Mexico) and baking with alkaline baking powder releases much of the nicotinic acid. This may explain why pellagra has always been rare in Mexico, despite the fact that maize is the dietary staple.
Up to 10% of the niacin in niacytin may be biologi-cally available as a result of hydrolysis by gastric acid.
Related Topics