Chapter: 11 th 12th std standard Bio Botany plant tree Biology Higher secondary school College Notes
Types of seed germination : Epigeal, Hypogeal germination, Vivipary
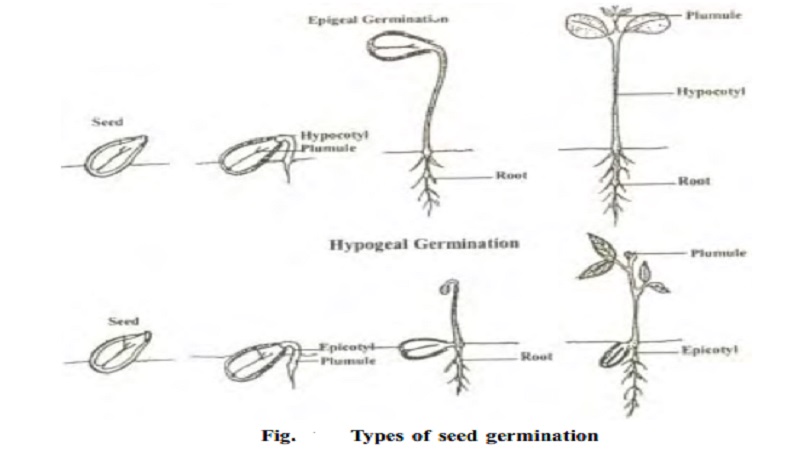
Types of seed germination
It is of two types.Epigeal and hypogeal.
Epigeal germination
In this type of germination, the cotyledons are brought above the ground due to rapid elongation of hypocotyl. Epigeal germination seen inmany dicotyledon seeds such as bean, castor, sunflower, gourd, cucumber etc., During this germination the hyphocotyl grows actively and become curved. It brings the seed above the soil. After coming above the surface of the soil, the hypocotyl straightens. The loosened seed coat fall down and the cotyledons become green. Now, the epicotyl grows and plumule gives rise to green leaves. The cotyledons fall down ultimately.
Hypogeal germination
In this type of germination, the cotyledons remain below the soil due to rapid elongation of epicotyl. It is found in many dicotyledonous seeds and monocotyledonous seeds. During this germination, the epicotyl elongates and become curved. It brings the plumule above the soil. Cotyledons remain underground. In case of monocotyledonous seeds like maize, the coleoptile (plumule covering) grows straight into the soil and comes out to form the green tube. Plumle elongates as well and comes out of the soil while contained in the coleoptile. the plumle ruptures the coleoptile with further growth. The coleorrhiza (covering of radicle) along with radicle grows downwards. After sometimes coleorrhiza ruptures due to further growth of the radicle. The radicle forms the primary root which is soon replaced by fibrous foot.
Special type of Germination
Vivipary
Vivipary is the special type of seed germination. During germinatin, seed is till attached to parent plant and nourished by it. Vivipary generally occurs in mangrove plant. The mangrove plants are generally medium sized tree which grow in salty marshes of sea coasts. (eg.Rhizophora, Sonneratia, Avicennia).The seeds of mangrove plants cannot germinate on themarshy habitat because of the excessive saltconcentration and lack of oxygen. The embryo of the seed continues growth while stillattached to parentplant. The radicle of the plant elongates considerably and projects out of the fruit. The lower part of the radicle becomes thick and swollen. Finally, dart like seedling breaks off the parent plant due to its incresing weight and gets embedded into the marsh in such a position that the plumule remains outside the satish water. The radicle immediately formsnew roots and establishes the seedling as a new plant.
Related Topics