Chapter: 12th Botany : Chapter 5 : Plant Tissue Culture
Types of Plant tissue cultures
Types of Plant tissue cultures
Based on the explants some other plant tissue culture types are
1. Organ culture
2. Meristem culture
3. Protoplast culture
4. Cell culture.
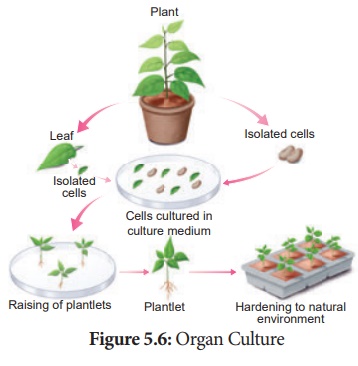
1. Organ culture
The culture of embryos, anthers, ovaries, roots, shoots or other
organs of plants on culture media.
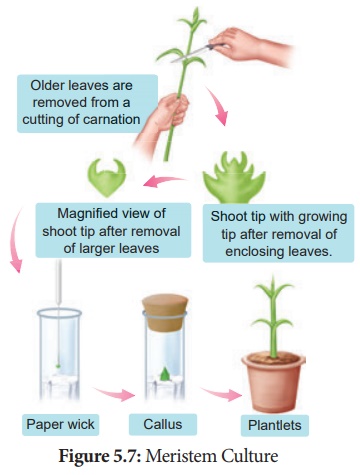
2. Meristem Culture:
The culture of any plant meristematic tissue on culture media.
3. Protoplast Culture:
Protoplasts are cells without a cell wall, but bounded by a cell
membrane or plasma membrane. Using protoplasts, it is possible to regenerate
whole plants from single cells and also develop somatic hybrids. The steps
involved in protoplast culture.
i. Isolation of protoplast: Small bits of plant tissue like leaf
tissue are used for isolation of protoplast. The leaf tissue is immersed in
0.5% Macrozyme and 2% Onozuka cellulase enzymes dissolved in 13% sorbitol or
mannitol at pH 5.4. It is then incubated over-night at 25°C. After a gentle
teasing of cells, protoplasts are obtained, and these are then transferred to
20% sucrose solution to retain their viability. They are then centrifuged to
get pure protoplasts as different from debris of cell walls.
ii. Fusion of protoplast: It is done through the
use of a suitable fusogen. This is normally PEG (Polyethylene Glycol). The
isolated protoplast are incubated in 25 to 30% concentration of PEG with Ca++
ions and the protoplast shows agglutination (the formation of clumps of cells)
and fusion.
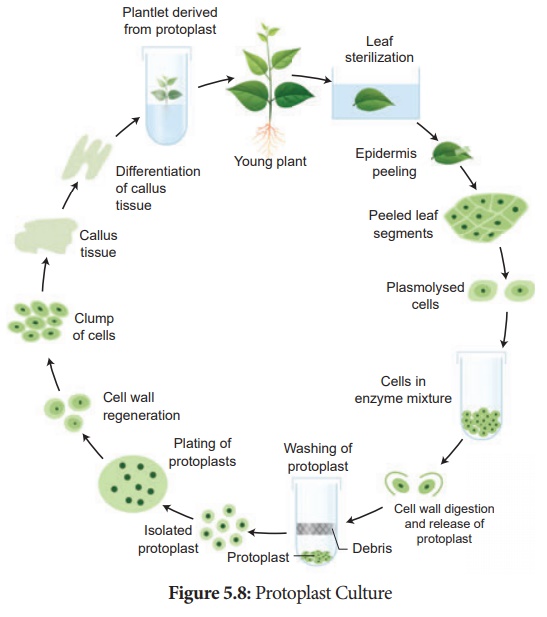
iii. Culture of protoplast: MS liquid medium is used
with some modification in droplet, plating or micro-drop array techniques.
Protoplast viability is tested with fluorescein diacetate before the culture.
The cultures are incubated in continuous light 1000-2000 lux at 25°C. The cell
wall formation occurs within 24-48 hours and the first division of new cells
occurs between 2-7 days of culture.
iv. Selection of somatic hybrid cells: The fusion
product of protoplasts without nucleus of different cells is called a cybrid.
Following this nuclear fusion happen. This process is called somatic
hybridization.
4. Cell Suspension Culture
The growing of cells including the culture of single cells or
small aggregates of cells in vitro in liquid medium is known as cell suspension
culture. The cell suspension is prepared by transferring a portion of callus to
the liquid medium and agitated using rotary shaker instrument. The cells are
separated from the callus tissue and used for cell suspension culture.
Production of Secondary Metabolites
Cell suspension culture can be useful for the production of
secondary metabolites like alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenoids, phenolic
compounds and recombinant proteins. Secondary metabolites are chemical
compounds that are not required by the plant for normal growth and development
but are produced in the plant as ‘byproducts’ of cell metabolism. For Example:
Biosynthesis and isolation of indole alkaloids from Catharanthus roseus plant
cell culture.
The process of
production of secondary metabolites can be scaled up and automated using
bio-reactors for commercial production. Many strategies such as
biotransformation, elicitation and immobilization have been used to make cell
suspension cultures more efficient in the production of secondary metabolites.
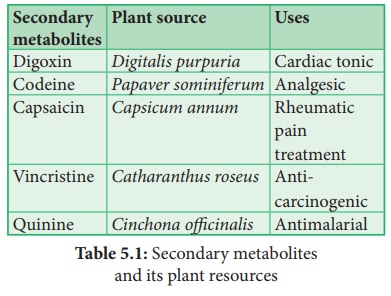
Few examples of industrially important plant secondary metabolites are listed
below in the table:
Related Topics