Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 5 : Hydrosphere
Tides
Tides
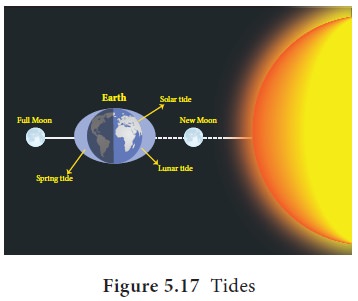
The rhythmic rise and fall of the sea water due to gravitational pull of the moon and the sun is called a Tide. Isaac Newton (1642– 1727) was the first person to explain tides scientifically. The rise of seawater towards the land is known as High tide or flow tide. The fall of seawater more towards sea is known as ‘Low tide water’ or ebb tide. On any day there will be two high tides and two low tides. The highest high tide occurs on full moon day and new moon day. It is known as spring tide (Figure 5.17). Spring tide happens when the sun, earth and moon aligned in straight line. The lowest low tide is known as neap tide. It happens when the sun, earth and moon are positioned at right angles.
The movement of ocean water as a result of tidal action is known as a tidal current. In places of narrow coastal inlet these tidal currents flow rapidly through the mouth with greater height and velocity. For example in the Bay of Fundy, between Nova Scotia and New Brunswick of Canada, the difference between high and low tides is as high as 14m. Ports which utilize the tidal current for entry and exit of ships from the harbour are known as tidal ports. In India Kolkatta and Kandla are examples of tidal harbours.
HOTS
Why does the highest Tide occur when the sun, earth and moon are aligned in a straight line?
The Gulf of Cambay and the Gulf of Kutch in Gujarat on the west coast have the maximum tidal range of 11m and 8m with average tidal range of 6.77m and 5.23m respectively. Tides help to clear the sediments deposited by rivers on their bed and thus prevent siltation of harbours. The energy of the tides is used to generate electricity. Tidal power stations have been set up in UK, Canada, France and Japan. In India Gulf of Khambhat, Gulf of Kutch and Sundarbans have scope for tidal energy production.
Fact File
A harbour is a sheltered water body where ships are anchored. A port is the area at the edge of a water body where boats and ships are docked, where transfer of goods and passengers take place and where trading is facilitated.
Related Topics