Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 5 : Hydrosphere
Salinity of the ocean
Salinity
of the ocean
Salinity
is defined as the
ratio between the weights of dissolved salts (in grams) per 1000 grams of water. It is
expressed as part per thousand (‰) and has no units. Example: 30‰ means 30
grams in 1,000 grams of sea water. The average ocean salinity is 35‰.
Sources
of salt in the ocean: Sea water is a weak but complex solution made up of many things including mineral
salts and decayed biological marine organisms. Most of the ocean salts are
derived from weathering and erosion of the earth’s crust by the rivers. Some of
the ocean salts have been dissolved from rocks and sediments below the sea
floor, while others have escaped from the earth’s crust through volcanic vents
as solid and gaseous materials.
Fact File
Depth of water is measured in the unit ‘Fathom’. One fathom is equal to
1.8 metre (six feet)
Factors affecting the salinity of ocean water
The salinity of ocean water depends
upon
1.
The rate of evaporation
2.
Amount of precipitation,
3.
Addition of fresh water flow from rivers
4.
Ice in Polar Regions
5.
Upwelling of deep water initiated by prevailing winds and
6.
Mixing of water by ocean currents.
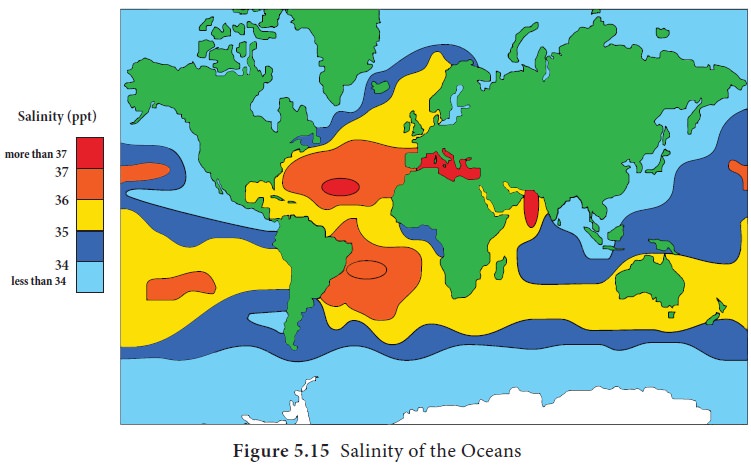
Distribution of salinity
On an average the salinity decreases
from equator towards the poles. The highest salinity is observed between 20°
and 40° north latitudes because this zone is characterized by high temperature,
high evaporation but less rain than the equatorial region.
The marginal areas of the oceans
bordering the continents have lower salinity than their interior due to
addition of fresh water to the marginal areas through the rivers (Figure 5.15).
Very high salinity is recorded in
Lake Von, Turkey (330‰ ) Dead Sea (238‰) and Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA (220‰).
Activity
Identify regions of high salinity and low salinity.
Compare the salinity of Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal and find the
reason for the same.
Find out the reason for low salinity on east coast of Asia and West
coast of North America.(Figure 5.15)
Why does the salinity vary along the west coast of South America?
Fact File
Isohaline is an imaginary line drawn to join places having equal
salinity.
Salinity of Dead
Sea is 8.6 times saltier than other
oceans. The shore of Dead Sea is 423m below sea level. It has the lowest
elevation on land. The sea is 377m deep. The high salt content will make people
float on the sea. The high salt content has made the Dead Sea devoid of life in
it.
Related Topics