Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 5 : Hydrosphere
Relief of ocean
Relief
of ocean
The bottom of the ocean has a variety of landforms just as it is seen on the earth’s surface. There are large mountain ridges, deep depressions, flat plains, basins and volcanoes. The configuration of an ocean floor is shown with the help of a ‘Hypsometric curve’ or ‘Hypsographic curve’. It is a graph denoting the proportion of a landmass standing above or below the sea level (Figure 5.7).
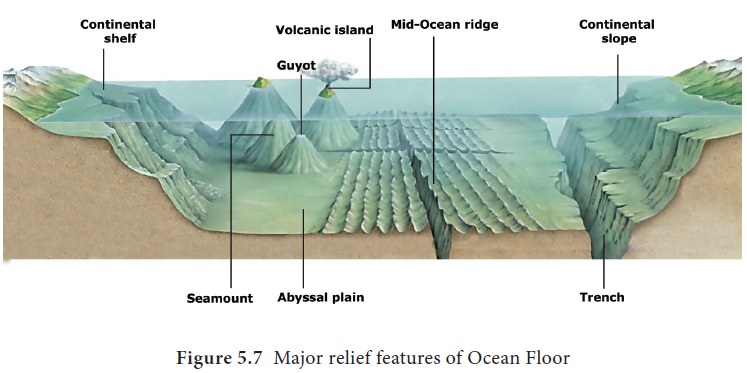
Continental shelf
Continental shelf is the seaward extension of land
that lies under the sea water. It occupies 7% of the sea floor. The continental
shelf slopes gently away from the land and is covered with shallow seas with an
average depth of 200
The width of the continental
shelf varies according to the nature of the rock beneath the crust. If the
crust is dynamic then the shelf would be narrow and vice versa. Continental
shelves are formed due to either any one or combination of the factors like
fluvial deposits, marine erosion, tectonic forces, and the fluctuations in sea
level in the past. Continental shelves are well known for oil, natural gas,
mineral deposits and coral reefs. World famous fishing grounds like Grand Bank
are situated here. The world’s widest continental shelf (1210 km long) is
located along the coast of Siberia, in Russia.
Continental shelf on the east coast
of India is formed by deltas of the Ganga, the Godavari, the Krishna and the
Cauvery. On the West coast of India the continental shelves are formed due to
faulting and consequent submergence.
Continental Slope
The zone of steep slope extending
from the continental shelf to the deep sea plain or abyssal plain is called
continental slope. The slope angle varies from 5° to 60°. It occupies 9% of sea
floor. This is the region in oceans where landslides, turbid currents, large
sediment slumps, under water canyons, gorges cut by the currents and rivers
occur. The deposit from the continental shelves immediately falls down here.
The origin of continental slope is believed to be due to erosional, tectonic
and aggradational processes.
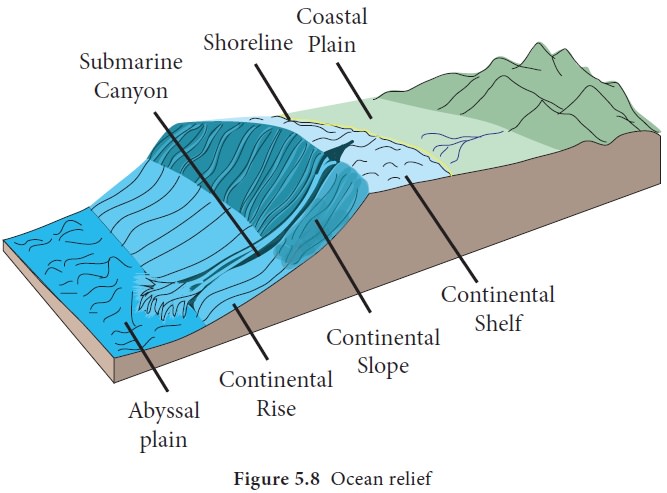
Continental rise
The area between the continental
slope and the sea floor is known as the continental rise. This part is noted
for the accumulation of sediments similar to the alluvial fans near the foot
hills in the land. It represents the boundary between continents and abyssal
plain. It constitutes about 5% of the oceanic area.
Abyssal plain
The Abyssal plain is the vast area of flat terrain in the bottom of the oceans. It is the largest part of ocean relief covering more than 50% of the total area.
There is an accumulation of very fine
sediments on the floor. The sediments are combinations of fine particles of
clay and microorganisms. As in the case of sedimentary rocks of earth’s surface
these sediments are in layers and are used to trace geological events in the
past.
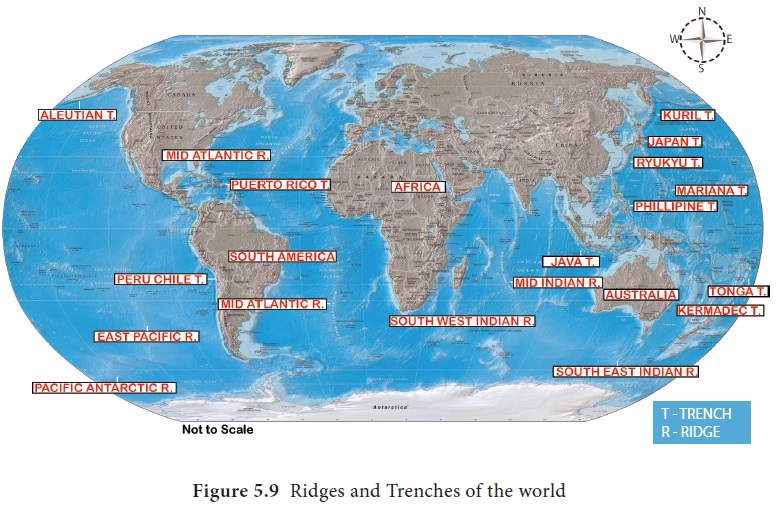
Mid oceanic ridges
The mid-ocean ridges are submarine
mountains. They are continuous and are connected to form a single global
mid-oceanic ridge system. They are formed by the tectonic forces acting from
within the earth. Mid oceanic ridges are located on the divergent plate
boundaries where magma flows through the fissure to form new oceanic crust.
They form the longest mountain range in the world extending for more than
56,000 km long and has a maximum width of 800–1,500 km.
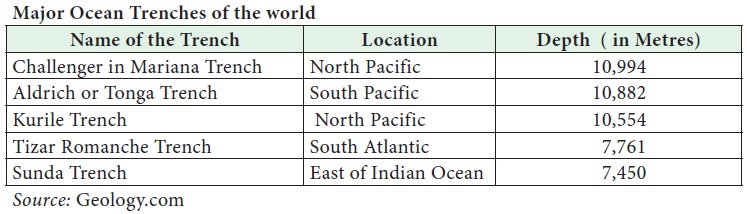
Ocean trench
The long, narrow, steep-sided
depressions formed by tectonic forces beneath the abyssal plain are called
Ocean trenches. Oceanic trenches actually extend 3 to 4 km below the level of
the abyssal plain. There are 26 oceanic trenches in the world: 22 in the
Pacific Ocean, 3 in the Atlantic Ocean and only one in the Indian Ocean. The
Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench, (10,994 m) in the Pacific Ocean is the
deepest part of the earth. A trench forms along the convergent boundary where
one plate subducts below the other (Figure 5.9).
Island
An island is a landmass surrounded by
water on all sides. Islands may be formed on the continental shelf or as
oceanic islands. Most of the oceanic islands are volcanic in origin. Group of
islands
Marine organisms, the coral polyps colonize the
tropical warm water and form islands known as coral islands. Lakshadweep Island in Indian Territory is made of
corals. Andaman Nicobar islands are of volcanic origin.
Guyots
Flat topped volcanic hills submerged under the
seawater are called guyots. It is a
part of an underwater chain of volcanic mountains produced by slow plate
movement.
Seamounts
Seamounts are conical, volcanic hills submerged
under ocean water. It does not reach to the water’s surface. It is an isolated
rise with an elevation of thousand metres or more from the surrounding sea
floor and with a limited summit area. It occupies 4.39 percent of ocean region.
Seamounts and guyots are most abundant in the North Pacific Ocean.
Bottom relief of Pacific Ocean
Continental shelf of the Eastern Pacific Ocean is
very narrow due to the presence of trenches while those on the western coast
are wide. Continental shelf adjoining coasts of Australia and Indonesia varies
in width from 160 to 1,600 km. In the Pacific Ocean, the abyssal plains are
very vast. Absence of mid oceanic ridges is the main reason for deep sea
plains. Prominent submarine ridges of the Pacific Ocean are Albatross plateau, Cocas ridge and Aleutian
ridge. Tasmania basin (New
Zealand ) and east pacific basin are major basins of Pacific Ocean. Pacific
Ocean has about 25,000 islands. There are number of archipelagos both in north
and south Pacific Ocean. The Hawaii islands were formed by hotspot. The
challenger deep in Mariana trench is the deepest part of Pacific Ocean
(10994m).
Bottom relief of Atlantic Ocean
In the North Atlantic Ocean, extensive continental
shelves are found around the shores of Newfoundland (Grand bank) and British
islands (Dogger Bank). In the South Atlantic Ocean, a very extensive
continental shelf is found between Bahia Blanca and Antarctica (Figure 5.10).
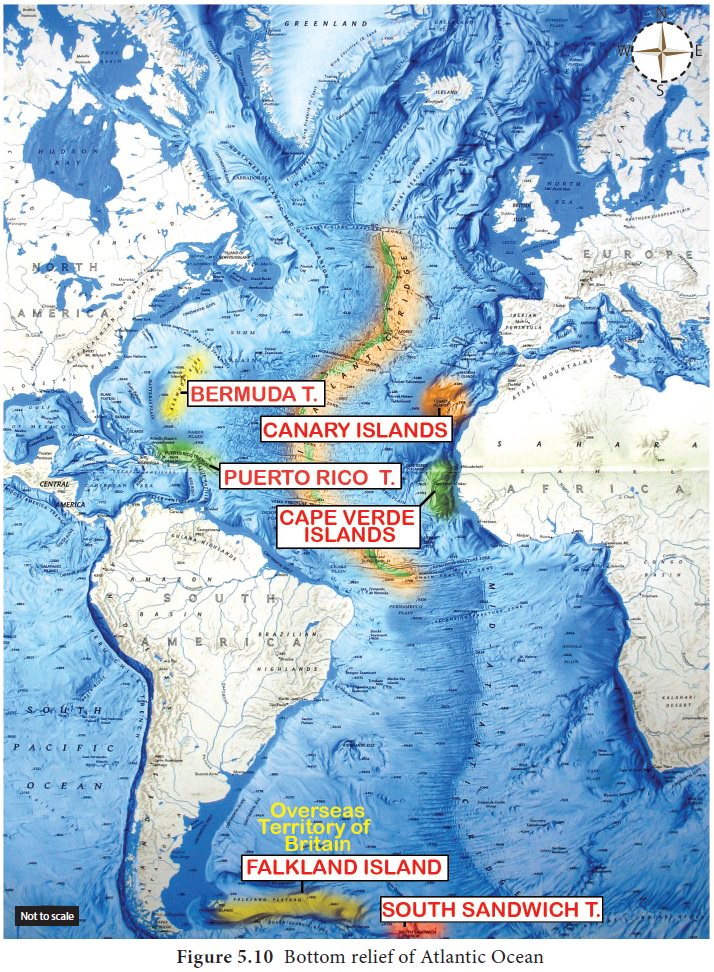
The most striking relief feature which is the ‘S’
shaped Mid–Atlantic ridge which extends for 16,000 km from Iceland in the north
to Bouvet Island in the south. The ridge separates the Eurasian Plate and North
American Plate in the North Atlantic, and the African Plate from the South
American Plate in the South Atlantic. Iceland
and Faroe are the few peaks of the
Mid-Atlantic ridge.
The mid-Atlantic ridge divides the Atlantic Ocean
into two major basins, i.e., East and West Atlantic basins. Other basins are
Spanish basin, north and south Canary basin, Guinea basin, Brazilian basin and
Labrador basin. Puerto Rico Deep (8,380
m) is the deepest of all deeps in
the Atlantic Ocean. Other deeps are Romanche
Deep and South Sandwich Trench.
The West Indies is an island archipelago near the
main land of North America. British Isles and Newfoundland are famous islands,
formed on the continental shelf in the North Atlantic Ocean. Sandwich island,
Georgia Island, Falkland and Shetland islands are islands in the South Atlantic
Ocean.
Bottom Relief of the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean has continental shelf of varying
width. Continental shelf along the coast of Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal and
Andaman varies in width from 192km to 280km. A variety of coral reefs thrive in
the warm tropical water of the Indian Ocean.
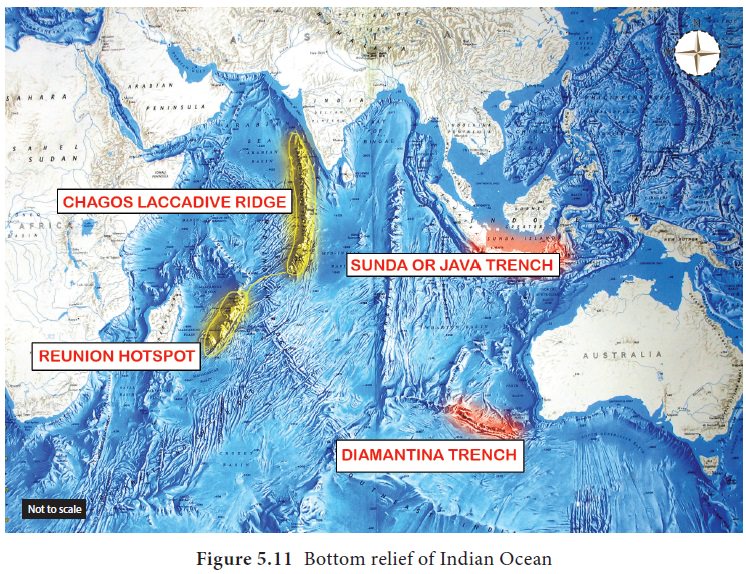
Indian Ocean has a continuous central ridge called
the Arabic Indian ridge. Other important ridges include the East Indian ridge,
West Australian ridge, South Madagascar ridge. Basins of Indian Ocean include Comoro basin, North Australian
basin, South Indian basin and the Arab basin (Figure 5.11).
The average depth of the Indian Ocean is 3890m.
Sunda deep near Java is the deepest part of this ocean (7450m). Madagascar and
Sri Lanka are the most prominent islands present in Indian Ocean. Andaman and
Nicobar islands in the Bay of Bengal are the raised part of mountains that are
the extension of Arakan Yoma which forms a part of Himalayas. Reunion Island is
located on a Hot spot.
Fact
File
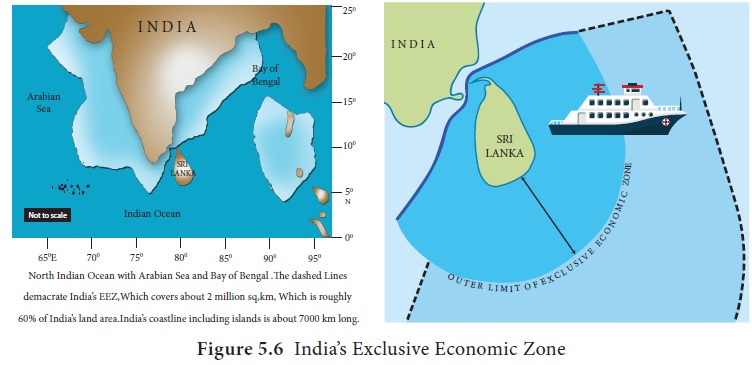
Indian
National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) with its Marine Satellite Information Services uses the
remotely sensed sea surface temperature (SST) to identify the locations of fish
aggregation. The details of the Potential Fishing Zones (PFZ) are then
disseminated to the fishermen once in every three days along the Indian Coast
by displaying the details in the Lighthouse in their respective regional
language (Figure 5.6).
Fact
File
Ocean
deep is grouped into two categories based on their size.
Very
deep but less extensive depression are called deeps. Long narrow linear and
more extensive depressions are called ‘trenches’.
Related Topics