Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 5 : Hydrosphere
Ocean Temperature
Ocean
Temperature
The measurement of degree of hotness or coldness of
ocean water is referred to as ocean temperature. Temperature is normally
measured in the unit of degree Celsius by thermometers. The major source of
heat energy for ocean water is the radiation from sun. The heating and cooling
capacity of water differs significantly from that of land.
Factors affecting horizontal distribution of ocean temperature
The factors affecting distribution of ocean
temperature are latitude, prevailing winds, ocean currents and local weather.
1. Latitude: The temperature of surface water decreases from equator towards the poles because of the slanting rays of the Sun pole ward.
2. Prevailing wind: Direction of the wind affects
the distribution of temperature of ocean water. The off shore winds blowing
from the land towards ocean or sea raise the temperature of ocean water. Winds
blowing from snow covered regions in winter lower the surface temperature. In
trade wind belt, the off shore winds initiate upwelling of cooler water from
beneath and on shore winds pile up warm water to increase the temperature to
certain extent.
3. Ocean currents: Warm currents raise the temperature
of the oceans where they flow whereas cold currents lower down the temperature.
Gulf Stream (warm current) increases the temperature of the eastern part of
North America and the west coast of Europe. Labrador cold current reduces the
temperature near north eastern coast of North America.
4. Apart from these, some minor factors like
submarine ridges, local weather conditions like storms, cyclones, hurricanes,
fog, cloudiness, evaporation and condensation also affect the surface
temperature of ocean water.
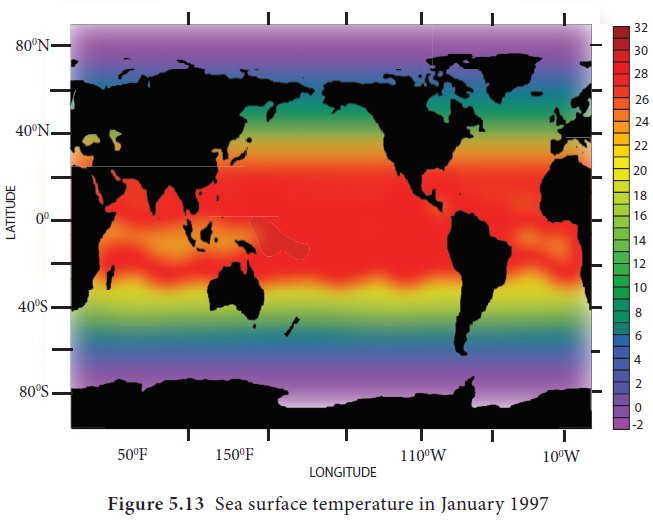
These images show the sea surface temperature in Celsius. The Figure 5.12 shows the sea surface temperature in July and the Figure 5.13 in January. Cold temperatures are shown in purple, moderate temperatures in aquatic green and warm temperatures in yellow to red. Landmass is shown by black colour. The diurnal range and annual range of temperature of ocean is much less than that of the land.
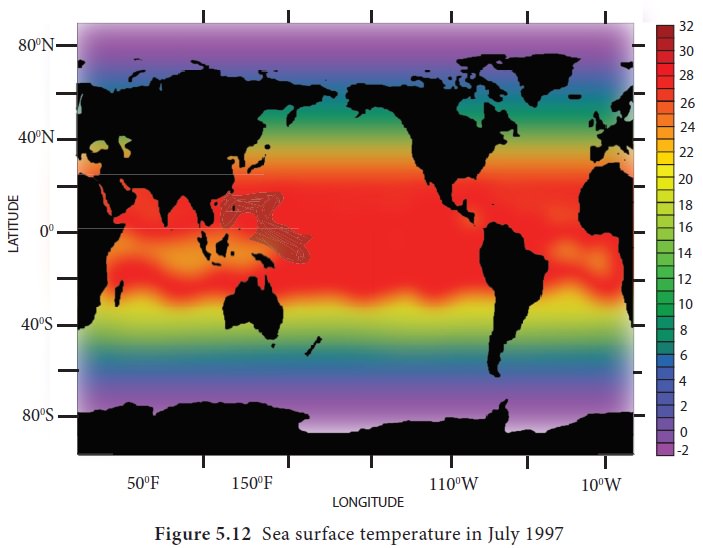
The temperature of the sea surface is highest (27°C to
30°C) not near Equator but few degrees north of the Equator. The lowest
temperature recorded is -1.9°C near the poles. The maximum and minimum annual
temperatures of ocean water are recorded in August and February in the Northern
hemisphere and reverse in case of the southern hemisphere.
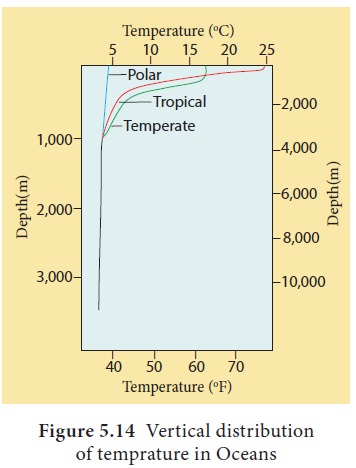
Vertical distribution of temperature in oceans
The uppermost layer of ocean water is warm and well mixed surface layer with average temperature between 20° and 25°C. The depth of this layer varies according to seasons. On an average this layer extends up to 200 m in tropical region. Beneath this layer lies the thermocline layer.
This
layer varies in depth between 200 metre to 1000 metre. This layer is unique
that the temperature decreases rapidly with increasing depth. Below the
thermocline temperature decrease is gradual up to 4000m. Beneath this depth the
temperature of ocean water is constant at 4°C (Figure 5.14).
Related Topics