Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 11 : Chemical Coordination and Integration
Thyroid gland
Thyroid gland
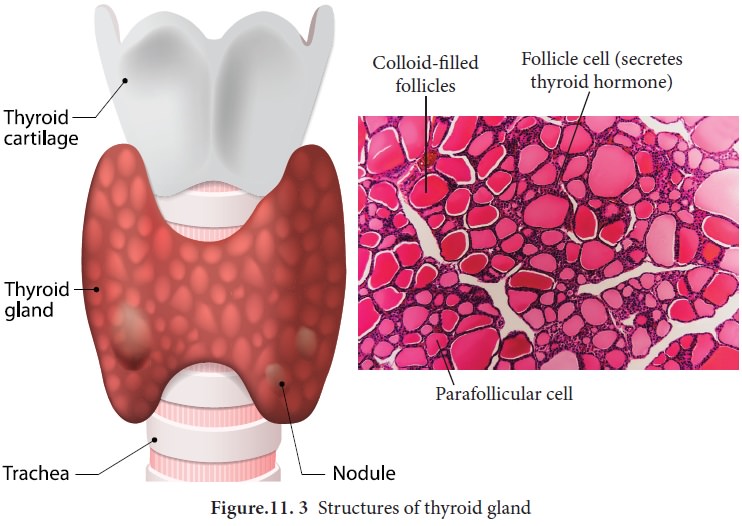
The butterfly shaped thyroid gland is a bilobed gland located below the larynx on each side of upper trachea. It is the largest endocrine gland in the body. Its two lateral lobes are connected by a median tissue mass called isthmus. Each lobe is made up of many lobules .The lobules consist of follicles called acini (acinus in singular). Each acinus is lined with glandular, cuboidal or squamous epithelial cells. The lumen of acinus is filled with colloid, a thick glycoprotein mixture consisting of thyroglobulin molecules.
Hormones of the thyroid gland are often called the
major metabolic hormones. The follicular cells of thyroid gland secrete two
hormones namely tri-iodothyronine (T3 ) and thyroxine or tetra-
iodothyronine (T4). The parafollicular cells or ‘C’ cells of thyroid
gland secrete a hormone called thyrocalcitonin. Iodine is essential for the
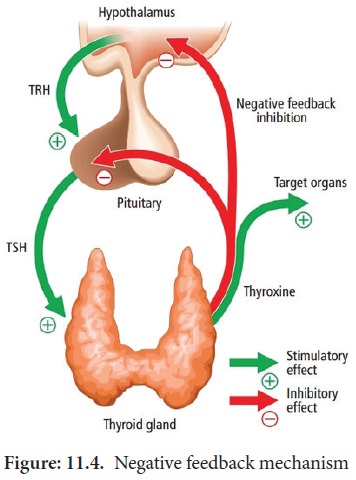
normal synthesis of thyroid hormones. Thyroid releasing hormone from the
hypothalamus stimulates the adenohypophysis to secrete TSH, which inturn
stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete the thyroid hormones. Thyroid hormones
show a negative feedback effect on the hypothalamus and pituitary (Figure11.
4).
Functions
of thyroxine or tetra-iodothyronine (T4): Thyroxine regulates the basal metabolic rate (BMR) and body heat
production. It stimulates protein synthesis and promotes growth. It is
essential for the development of skeletal and nervous system. Thyroxine plays
an important role in maintaining blood pressure. It reduces serum cholesterol
levels, Optimum levels of thyroxine in blood is necessary for gonadial
functions.
Functions
of thyrocalcitonin (TCT): TCT is a polypeptide hormone, which regulates the blood calcium and phosphate
levels. It reduces the blood calcium level and opposes the effects of
parathyroid hormone.
Related Topics