Hormones of adenohypophysis, neurohypophysis - Pituitary gland or Hypophysis | 11th Zoology : Chapter 11 : Chemical Coordination and Integration
Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 11 : Chemical Coordination and Integration
Pituitary gland or Hypophysis
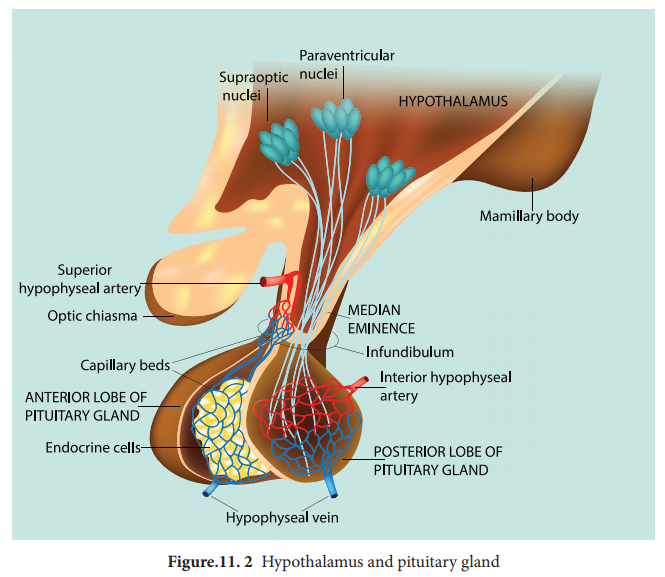
Pituitary gland or Hypophysis
The pituitary gland (means to grow under) is ovoid
in shape and is located in the sella
turcica, a bony cavity of the
sphenoid bone at the base of brain and connected to the hypothalamic region of the brain by a stalk called infundibulum. It is about one
centimetre in diameter and 0.5 gm in weight. The pituitary consists of two
lobes, anterior glandular adenohypophysis and posterior neural neurohypophysis.
The anterior lobe originates from the embryonic invagination of pharyngeal
epithelium called Rathke’s pouch and
the posterior lobe is originates from the base of the brain as an outgrowth of
hypothalamus. Anatomically the adenohypophysis has three lobes or zones namely
pars intermedia, pars distalis and pars tuberalis. The neurohypophysis is
otherwise known as pars nervosa.
The anterior lobe of pituitary secretes six tropic
hormones such as growth hormone (GH), thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), adreno
corticotropic hormone (ACTH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH),
luteinizing hormone (LH), luteotropic hormone (LTH) and melanocyte stimulating
hormone (MSH) (in lower animals only). The posterior lobe of pituitary secretes
the hormones namely vasopressin and oxytocin.
Hormones of Adenohypophysis
(i) Growth hormone (GH): It is also known as somatotropic hormone (STH) or Somatotropin. It is a peptide hormone. Growth hormone promotes growth of all the tissues and metabolic process of the body. It influences the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids and increases the rate of protein biosynthesis in the cells. It stimulates chondrogenesis (cartilage formation), osteogenesis (bone formation) and helps in the retention of minerals like nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus, sodium etc., in the body. GH increases the release of fatty acid from adipose tissue and decreases the rate of glucose utilization for energy by the cells. Thus it conserves glucose for glucose dependent tissues, such as the brain.
ii)
Thyroid
stimulating hormone (TSH) or thyrotropin: TSH is a glycoprotein hormone, which stimulates the thyroid gland to
secrete Tri-iodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). TSH secretion is regulated
by negative feedback mechanism.
It’s release from the anterior
pituitary is induced by the thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH). When thyroxine
level in the blood increases, TRH acts on both the pituitary and hypothalamus
to inhibit TSH secretion.
(iii) Adreno
cortico tropic hormone (ACTH): ACTH is a peptide hormone that stimulates the adrenal cortex to
secrete glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. It stimulates melanin synthesis
in melanocytes, induces the release of fatty acids from adipose tissues and
stimulates insulin secretion. ACTH secretion is regulated by negative feedback mechanism.
(iv) Follicle
stimulating hormone (FSH): FSH is a glycoprotein hormone which regulates the functions of the gonads
(ovary and testis). In males, FSH along with androgens acts on the germinal
epithelium of seminiferous tubules and stimulates the production and release of
sperms (spermatogenesis). In females, FSH acts on the ovaries and brings about
the development and maturation of graffian follicles.
(v) Luteinizing
hormone (LH): LH is a glycoprotein hormone which is also known as interstitial cell stimulating hormone
(ICSH). In males, ICSH acts on the interstitial cells of testis to produce the
male sex hormone, testosterone. In females, LH along with FSH matures the
ovarian follicles. LH independently induces ovulation, maintains the corpus
luteum and promotes synthesis and release of ovarian hormones. FSH and LH are
collectively referred as gonadotropins. FSH and LH are not produced during
childhood. The secretion of FSH and LH starts only during pre pubertal period.
(vi) Luteotropic
hormone (LTH): LTH is also called luteotropin or lactogenic
hormone or prolactin or mammotropin.
It is a protein hormone which stimulates milk secretion after the child birth
in females. High prolactin secretion during lactation suppresses LH secretion
and ovulation since it induces the corpus luteum hence named as luteo tropic
hormone.
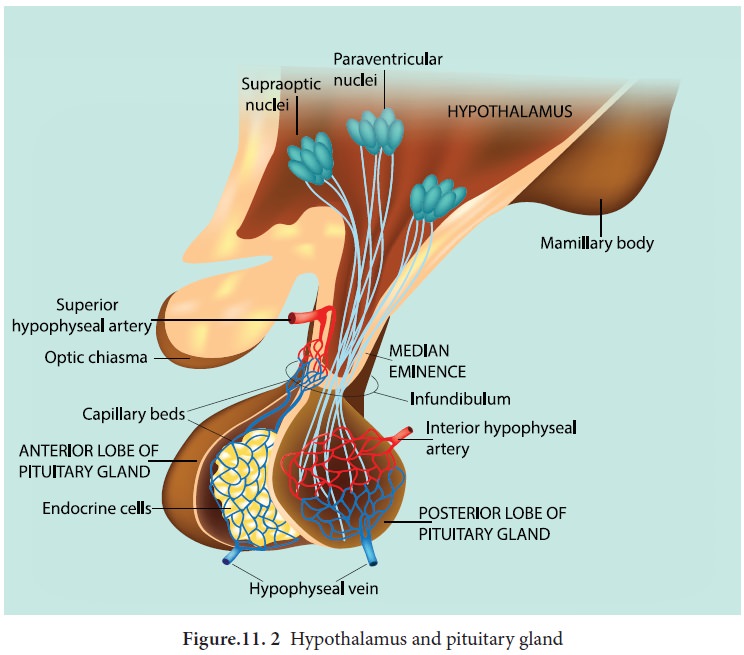
Hormones of neurohypophysis
i. Vasopressin
or antidiuretic hormone (ADH) : ADH is a peptide hormone which promotes reabsorption of water and
electrolytes by distal tubules of nephron and thereby reduces loss of water
through urine. Hence it is called as anti diuretic hormone. It also causes
constriction of blood vessels when released in large amount and increases blood
pressure. ADH deficiency causes Diabetes insipidus which induces the
production of large amount of urine.
ii. Oxytocin
(means
quick birth): It is a peptide hormone which stimulates vigorous contraction of the smooth muscles of
uterus during child birth and ejection of milk from the mammary glands.
Related Topics