Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 11 : Chemical Coordination and Integration
Mechanism of hormone action
Mechanism of hormone action
Hormones circulate in the blood but their concentration can increase or decrease based on the requirement of the body. This is controlled by feedback mechanisms.
These mechanisms control the secretion of
endocrine glands by stimulating the hypothalamus, pituitary or both, which
inturn governs the secretion of a particular hormone. In positive feedback, the
secretion of the hormone increases where as in negative feedback further
secretion of hormone slows down. Feedback mechanisms are the key factors for
maintaining homeostasis in our body.
Hormones are classified into three major groups as
peptide hormones, steroid hormones and amino acid derived hormones based on
their chemical structure.
·
Peptide hormones cannot cross the phospolipid cell
membrane and bind to the receptors on the exterior cell surface. They are are
transported to the golgi, which is the site of modification. It acts as a first messenger in the cell. Hormones
on binding to their receptors do not enter the target cell but generate the
production of second messengers such
as cyclic AMP (c AMP), which in turn regulates cellular metabolism. This is catalyzed by the enzyme adenylate cyclase. The interaction between the hormone at the
surface and the effect brought out by cAMP within the cell is known as
signaling cascade. At each step there is a possibility of amplification. (Figure
11.17)
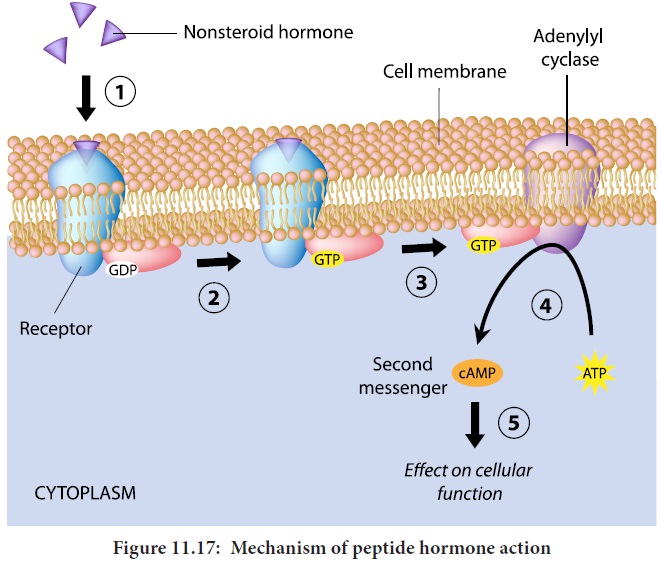
1.One hormone molecule may bind to multiple receptor molecules before it is degraded.
2.Each receptor may activate several adenylate
cyclases each of which make much c AMP.
3.Thus there is more signal after each step.
The actions of cAMP are terminated by
phosphodiesterases. The effect of peptide hormones like insulin, glucagon,
somatotropin are usually short lived because they work through second messenger
system.
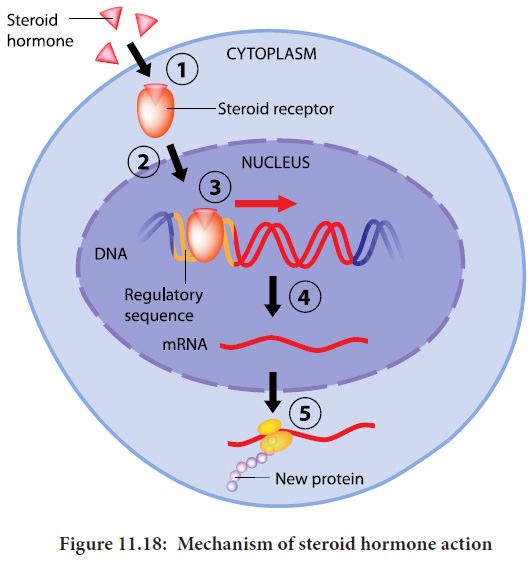
· Steroid hormones can easily cross the cell
membrane, and bind to their receptors, which are intracellular or intranuclear.
Upon binding to the receptors, they pair up with another receptor – hormone
complex (dimerize).This dimer can then bind to DNA and alter its transcription.
(Figure 11.18)
· The effect of steroid hormones such as aldosterone,
oestrogen, FSH are long lived, as they alter the amount of mRNA and protein in
a cell.
· Amino acid derived hormones are derived from one or
two aminoacid with a few additional modifications. Thyroid hormone is
synthesised from tyrosine and includes the addition of several iodine atoms.
Epinephrine an amino acid derivative may function through second messenger
system like peptide hormones or they may actually enter the cell and function
like steroid hormones.
Related Topics