Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 11 : Chemical Coordination and Integration
Pancreas
Pancreas
Pancreas is a composite gland which performs both
exocrine and endocrine functions.
It is located just below the stomach as a leaf like
structure. The pancreas is composed of two major tissues such the acini and
islets of langerhans. Acini secretes digestive enzymes and the islets of
langerhans secretes hormones like insulin and glucagon.
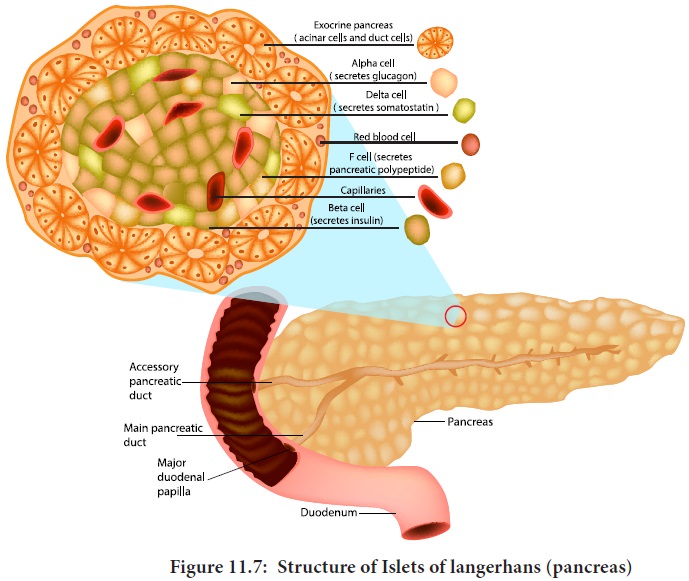
Human pancreas has one to two million islets of langerhans. In each islet about 60% cells are beta cells, 25% cells are alpha cells and 10% cells are delta cells. The alpha cells secrete glucagon, the beta cells secrete insulin and delta cells secrete somatostatin.
Insulin: Insulin
is a peptide hormone and plays an important role in glucose homeostasis. It’s main effect is to lower blood glucose levels by
increasing the uptake of glucose into the body cells,
especially muscle and fat cells. Insulin also inhibits the breakdown of
glycogen to glucose, the conversion of amino acids or fats to glucose, so
insulin is rightly called a hypoglycemic hormone.
Glucagon:
Glucagon
is a polypeptide hormone. It is a potent hyperglycaemic hormone that acts on the liver and promotes the breakdown of
glycogen to glucose (Glygogenolysis), synthesis of glucose from lactic acid and
from non-carbohydrate molecules (Gluconeogenesis) . Glucagon releases glucose
from the liver cells, increasing the blood glucose levels. Since glucagon
reduces the cellular uptake and utilisation of glucose it is called a
hyperglycemic hormone. Prolonged hyperglycemia leads to the disorder called
diabetes mellitus.
Related Topics