Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 11 : Chemical Coordination and Integration
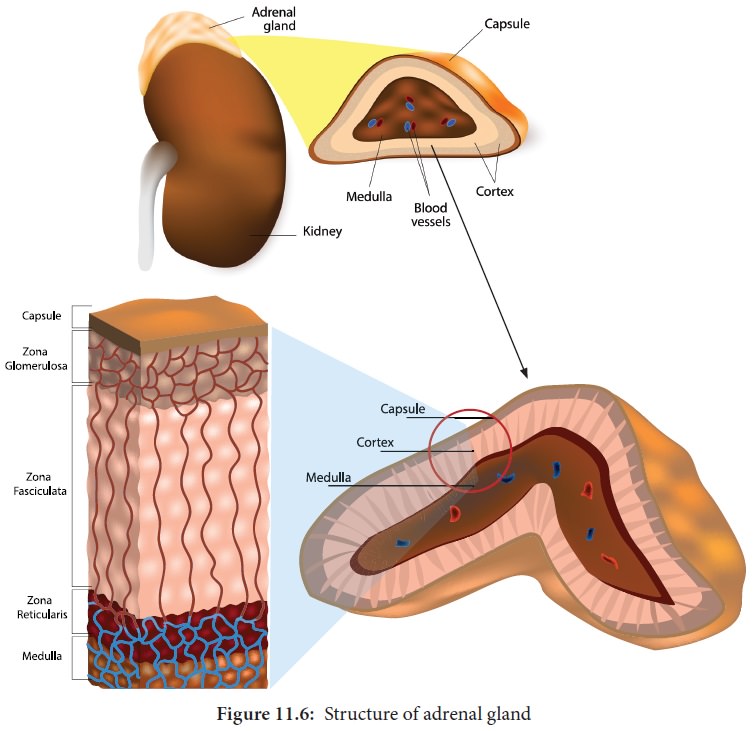
Adrenal gland
Adrenal gland
A pair of adrenal glands are located at the
anterior end of the kidneys, hence also called suprarenal glands. Anatomically
the outer region is the cortex and the inner region is the medulla.
Histologically the adrenalcortexhasthreedistinctzones,zona glomerulosa, zona
fasciculata and zona reticularis. Zona
glomerulosa an outer thin layer constitutes about 15% of adrenal cortex,
and secretes mineralocorticoids. Zona
fasciculata, the middle widest layer
constitutes about 75% of adrenal cortex and
secretes glucocorticoids such as cortisol, corticosterone and trace amounts
of adrenal androgen and oestrogen. Zona
reticularis, an inner zone of adrenal cortex constitute about 10% of
adrenal cortex and secretes the adrenal androgen, trace amount of oestrogen and
glucocorticoids.
Adrenal medulla: It is the central part of adrenal gland and is composed of ovoid and columnar cells, which are found around the network of blood capillaries. Adrenalin (epinephrine) and nor adrenalin (nor epinephrine) are the two hormones secreted by the adrenal medulla. Both adrenalin and nor adrenalin are catecholamines.
Function
of adrenal hormones:
Glucocorticoids stimulate gluconeogensis, lipolysis and proteolysis (the life saving activity). Cortisol is a glucocorticoid involved in maintaining cardio
vascular and kidney functions. It produces anti-inflammatory reactions and
suppresses the immune response. It stimulates the RBC production. It is also
known as stress combat hormone. Mineralocorticoids
regulates water and electrolyte balance of our body. Aldosterone stimulates the reabsorption of sodium and water and
eliminates potassium and phosphate ions through excretion, thus it helps in
maintaining electrolytes, osmotic pressure and blood pressure. Adrenal androgen
plays a role in hair growth in the axial region, pubis and face during puberty.
The adrenal
medulla secretes the hormones adrenalin and noradrenalin and are referred
as "3F hormone" (fight, flight and fright hormone). Adrenalin
increases liver glycogen breakdown into glucose and increases the release of
fatty acids from fat cells. During emergency it increases heart beat rate and
blood pressure. It stimulates the smooth muscles of cutaneous and visceral
arteries to decrease blood flow. It increases blood flow to the skeletal
muscles thereby increases the metabolic rate of skeletal muscles, cardiac
muscles and nervous tissue.
Related Topics