Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Textiles And Dress Designing Cloth stitch Higher secondary school College practical steps methods Notes
Thread Count and Basic Weave Structures
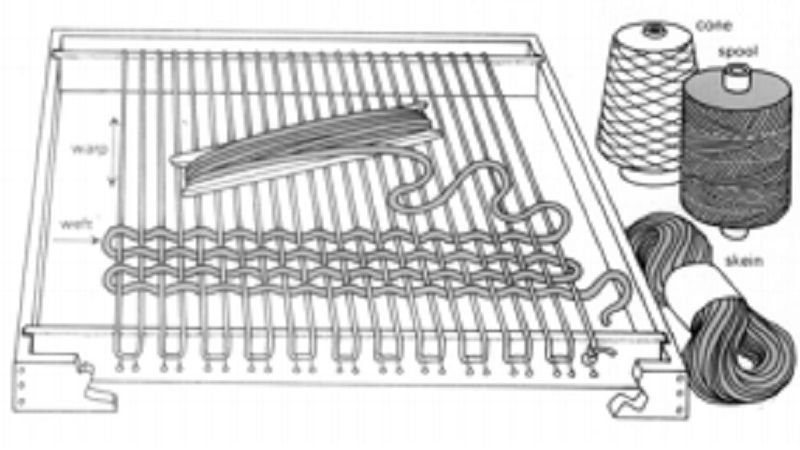
Thread Count:
Thread count or fabric count is determined by counting the number of warp (Ends) and wefts (picks) per square inch of fabric. Higher the thread count more compact will the fabric be; so it will be more strong and durable. A fabric with high thread count will be more costly. It is denoted by X � Y, eg., 50 �30. Compact fabric shrinks less. Based on thread count there exists balanced and unbalanced constructions. When number of warp yarns are equal or nearly equal to the number of weft yarns, the construction is balanced and when the difference between the number of warp and weft yarns will be very large than that construction will be an unbalanced construction.
Durability of fabric depends on the following factors:
Natural fibers or man-made fibers.
Kind and quality (staple or filament)
Strength and twist of yarn
Single, ply, cord, decorative or uniform yarns.
Compactness of construction or thread count.
Kind of weave.
Basic Weave Structures:
The manner in which groups of warp yarns are raised by the harness to permit the insertion of the filling yarn determines the pattern of the weave, and in large measure the kind of fabric produced. Weave patterns can create varying degrees of durability in fabrics, adding to their usefulness and also to their appearnance.
There are three basic weaves. They are plain weave, twill weave and satin weave. All other weaves are a variation or a combination of these weaves. Basket weave and Rib weave are two variations of plain weave. In the same manner twill weave can also have number of variations, e.g., warp faced twill, weft faced twill, even twill, uneven twill, pointed twill, herring bone twill, gabardine, corkscrew and so on.
Graph paper (or pointed paper) is used to show the weaves or the order in which the Representation of Plain Weave yarns interlace in a fabric. It is used by textile designers to portray their designs or to analyse fabric weaves. Each vertical row of squares represents a warp yarn and each horizontal row of squares represents a filling yarn. A warp yarn crossing over a fillings usually shown by marking in the square
Related Topics