Chapter: Clinical Dermatology: Regional dermatology
The mouth and genitals
The mouth
and genitals
Mucous
membranes are covered with a modified stratified squamous epithelium that lacks
a stratum corneum. This makes them moist and susceptible to infection, and to
conditions not seen elsewhere. In contrast, the skin around them is like that
on other body sites, and develops the standard range of skin disorders. It
follows that the diagnosis of puzzling mouth or genital changes is often made
easier by look-ing for skin disease elsewhere.
The mouth
The
mouth can harbour an enormous range of dis-eases, affecting each of its
component structures. Inflammatory and infectious disorders of the mouth are
usually either red or whitealeading to the terms erythroplakia and leukoplakia,
respectively. These are descriptive terms but not diagnoses. A biopsy will help
sort out the non-dysplastic causes, such as lichen planus and candida
infections, from the dysplastic ones that are the precursors of carcinoma.
Some
skin diseases cause ulceration in the mouth. These ulcers are accompanied by
skin diseases else-where on the body, and making a diagnosis there is easier
than in the mouth. In other patients with mouth ulcers, the course of the ulcers
or erosions, and their size and location in the mouth, provide diagnostic
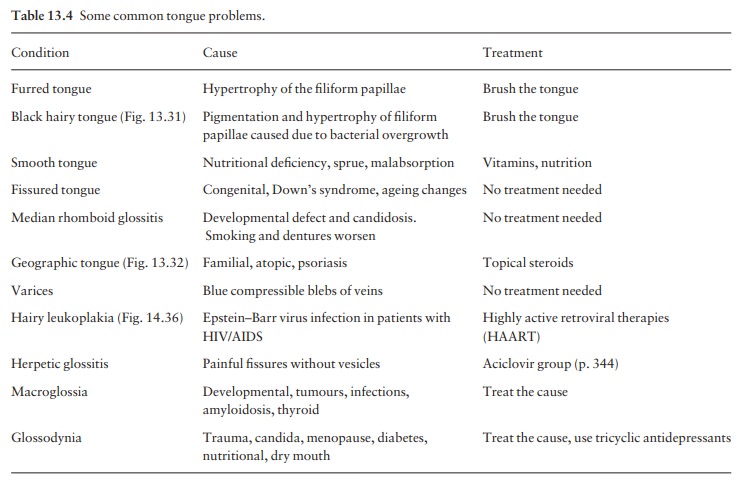
clues. Table 13.4 lists some common tongue troubles.
Related Topics