Sampling Techniques and Statistical Inference - Summary | 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 8 : Sampling Techniques and Statistical Inference
Chapter: 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 8 : Sampling Techniques and Statistical Inference
Summary
Summary
·
Sampling: It is the procedure or process of
selecting a sample from a population.
·
Population: The group of individuals considered
under study is called as population.
·
Sample :Aselection of a group of individuals
from a population.
·
Sample size :The number of individuals included in a
sample.
·
Simple Random Sampling :The samples are
selected in such a way that each and every unit in the population has an
equal and independent chance of being selected as a sample.
·
Stratified Random Sampling: When the population is heterogeneous, the population is divided into homogeneous number of sub-groups or
strata. A sample is drawn from each stratum at random.
·
Systematic Sampling: Select the first sample at random, the rest being automatically selected according to some predetermined pattern.
·
Sampling Distribution: Sampling distribution of a statistic is the frequency distribution which is formed with various values of a statistic
computed from different samples of the same size drawn from the same
population.
·
Standard Error: The standard deviation of the sampling
distribution of a statistic is known as its Standard Error.
·
Statistical Inference: To draw inference about a population of any statistical investigation from the analysis of samples drawn from that
population.
·
Estimation :The method of obtaining the most likely
value of the population parameter using statistic is called
estimation.
·
Point Estimation: When a single value is used as an
estimate, it is called as point estimation.
·
Interval Estimation: An interval within which the parameter would be expected to lie is called interval estimation.
·
Test of Statistical Hypothesis: Statistical technique to arrive at a decision in certain situations where there is an element of uncertainty on the
basis of sampl
·
Null
Hypothesis: The hypothesis which is tested for
possible rejection under the assumption that it is true”, denoted by H0.
·
Alternative
Hypothesis:The hypothesis which is complementary to
the null hypothesis is called as the
alternative hypothesis, denoted by H1 .
·
Type
I error: The error of rejecting H0 when it is true.
·
Type
II error: The error of accepting H0 when it is false.
·
Test
of significance for single mean:
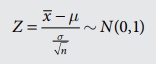
Related Topics