Sampling Techniques and Statistical Inference - Choose the correct Answer | 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 8 : Sampling Techniques and Statistical Inference
Chapter: 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 8 : Sampling Techniques and Statistical Inference
Choose the correct Answer
Choose the correct Answer
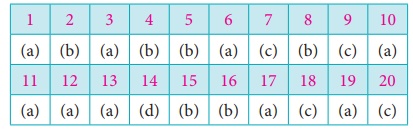
1. A …………. may be finite or infinite
according as the number of observations or items in it is finite or infinite.
(a)
Population
(b) census
(c) parameter
(d) none of these
2. A ……… of statistical individuals in a
population is called a sample.
(a) Infinite set
(b)
finite subset
(c) finite set
(d) entire set
3. A finite subset of statistical
individuals in a population is called ………...
(a)
a sample
(b) a population
(c) universe
(d) census
4. Any statistical measure computed from
sample data is known as …………...
(a) parameter measure
(b)
statistic
(c) infinite measure
(d) uncountable
5. A…………..is one where each item in the
universe has an equal chance of known opportunity of being selected.
(a) Parameter
(b)
random sample
(c) statistic
(d) entire data
6. A random sample is a sample selected
in such a way that every item in the population has an equal chance of being
included
(a)
Harper
(b) Fisher
(c) Karl Pearson
(d) Dr. Yates
7. Which one of the following is
probability sampling
(a) purposive sampling
(b) judgment sampling
(c)
simple random sampling
(d) Convenience sampling
8. In simple random sampling from a population
of units, the probability of drawing any unit at the first draw is
(a) n/N
(b)
1/N
(c) N/n
(d) 1
9. In …………….. the heterogeneous groups
are divided into homogeneous groups.
(a) Non-probability sample
(b) a simple random sample
(c)
a stratified random sample
(d) systematic random sample
10. Errors in sampling are of
(a)
Two types
(b) three types
(c) four types
(d) five types
11. The method of obtaining the most
likely value of the population parameter using statistic is called ……………………
(a)
estimation
(b) estimator
(c) biased estimate
(d) standard error.
12. An estimator is a sample statistic
used to estimate a
(a)
population parameter
(b) biased estimate
(c) sample size
(d) census
13. …………..is a relative property, which states
that one estimator is efficient relative to another.
(a)
efficiency
(b) sufficiency
(c) unbiased
(d) consistency
14. If probability P[| θ − θ |< ε] →
1µ as n → ∞′ , for any positive ε then θ is said to …………..estimator of θ .
(a) efficient
(b) sufficient
(c) unbiased
(d)
consistent
15. An estimator is said to be …………. if
it contains all the information in the data about the parameter it estimates.
(a) efficient
(b)
sufficient
(c) unbiased
(d) consistent
16. An estimate of a population
parameter given by two numbers between which the parameter would be expected to
lie is called an……………..interval estimate of the parameter.
(a)point estimate
(b)
interval estimation
(c) standard error
(d) confidence
17. A ________ is a statement or an
assertion about the population parameter.
(a)
hypothesis
(b) statistic
(c) sample
(d) census
18. Type I error is
(a) Accept H0 when it is true
(b) Accept H0 when it is
false
(c)
Reject H0 when it is true
(d) Reject H0 when it is
false.
19. Type II error is
(a)
Accept H0 when it is wrong
(b) Accept H0 when it is true
(c) Reject H0 when it is true
(d) Reject H0 when it is false
20. The standard error of sample mean is
(a)
σ /√2n
(b) σ /n
(c)
σ /√n
(d) s2/√n
Related Topics