Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Home Science Maintain Basic Knowledge for family life Higher secondary school College
Structure of the Kidney and Nephron
During the vital activity of the human and animal body, significant
amounts of organic degradation products are produced, a proportion of which is
not being utilized by cells. These degradation products must be eliminated from
the body. The end products of metabolism which have to be removed from the body
are called excreta, and the organs
that remove them are called excretory organs.
The lungs
eliminate carbon-di-oxide and water vapour into the environment. The
gastro-intestinal tract excretes a small amount of water, bile acids, pigments,
cholesterol, certain drugs (when administered into the body) salts of heavy
metals (Cadmium, iron, manganese) and indigestible food residues (faeces).
The skin performs its excretory function by sweat and sebaceous glands.
Sweat glands excrete sweat which contains water, salts, urea, uric acid,
creatinine and other compounds.
The main
excretory organs are the kidneys, which eliminate in the urine most of the
metabolites, primarily those containing nitrogen (Urea, Ammonia, Creatinine).
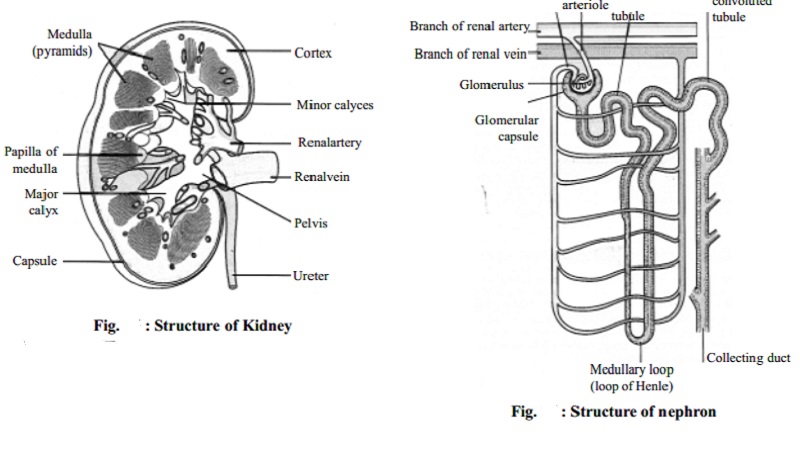
Structure of the Kidney
The kidney
is a bean-shaped organ about 5 cms long, 3 cms wide and 2 cms thick. There are
two kidneys which are situated at both sides of the lumbar area. The weight of
a kidney is about 200-250 gms. On the inner or medial border there is a notch
called the hilum at which region the
artery, the vein and the ureter connect with the kidney.
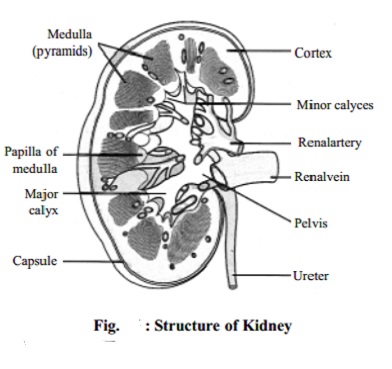
Each kidney has a pelvis, where the urine collects. The
urine is drained off from the pelvis by the ureters. The ureters end
in the urinary bladder which can hold about 800 ml of urine. The urethra
carries the urine from the bladder and voids it at convenient intervals.
In a longitudinal section, the kidney is seen to consist of outer cortex and inner medulla. The medulla consists of 10-18 conical or pyramidal shaped structures, known as
the renal pyramids. The base of a
renal pyramid faces towards, the cortex. The pelvis is the funnel-shaped upper end of the ureter.
Structure of the Nephron
The kidney substance is composed of about 1 million functional units,
the nephrons, and a smaller number
of collecting tubules. The uriniferous tubules are supported
by a small amount of connective tissue, containing blood vessels, nerves and
lymph vessels.
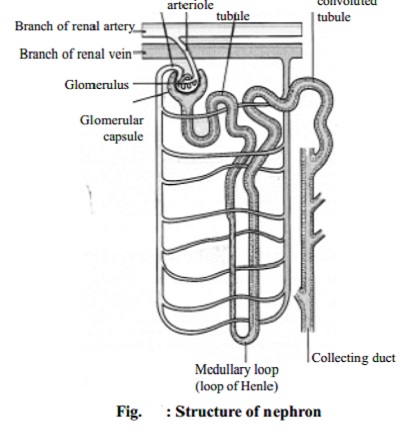
The nephron
The nephron consists of a tubule closed at one end, the other end
opening into a collecting tubule. The closed or blind end is indented to form
the cup-shaped glomerular capsule
(Bowman's capsule) which almost completely encloses a network of arterial
capillaries, the glomerulus. Continuing from the glomerular capsule
the remainder of the nephron is described in three parts: the proximal
convoluted tubule, the loop of Henle and the distal convoluted
tubule, leading into a collecting
tubule.
After entering the kidney at the hilus the renal artery divides into
smaller arteries and arterioles. In the cortex an arteriole, the afferent arteriole, enters each
glomerular capsule then subdivides into
a cluster of capillaries, forming the glomerulus. The blood vessel leading away
from the glomerulus is the efferent
arteriole; it breaks up into a second capillary network to supply oxygen
and nutritional materials to the remainder of the nephron. The blood pressure
in the glomerulus is higher than in other capillaries because the calibre of
the afferent arteriole is greater than that of the efferent arteriole.
Functions of the Kidney
Urine formation
Maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance
Disposal of waste material from the body
Related Topics