Chapter: Clinical Dermatology: Regional dermatology
Some other oral lumps, bumps and colour changes
Some other oral lumps, bumps and
colour changes
•
Mucocoeles are collections of mucin
following the rupture of a minor salivary gland duct. They are blue-tinted soft
translucent nodules, usually of the lips, and arise suddenly without pain.
•
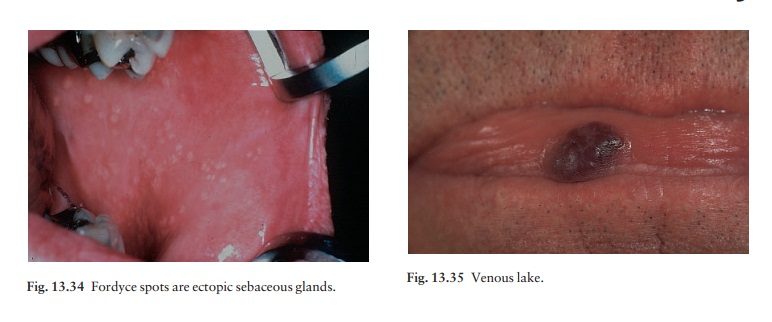
Fordyce spots are ectopic sebaceous
glands, appear-ing as pinhead-sized whitish-yellow papules on the labial mucosa
(Fig. 13.34).
•
Yellow patches in the mouth may
suggest pseudox-anthoma elasticum.
•
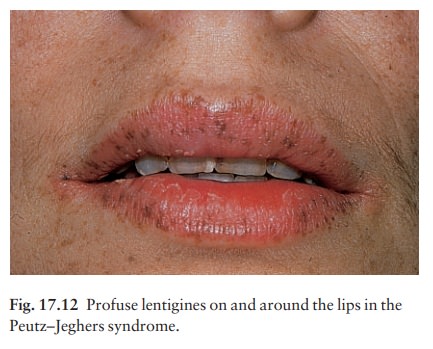
Brown macules on the lips should
trigger thoughts about the dominantly inherited Peutz–Jehgers syn-drome (Fig.
17.12) and its bowel polyps and tumours.
Neurofibromas
may occur, especially in patients with widespread cutaneous neurofibromatosis.
•
Telangiectases may suggest
hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. These patients may also have
telangiec-tases in their intestinal tract leading to gastrointestinal bleeding,
and arteriovenous fistulae especially in the lungs that may lead to cerebral
embolism.
•
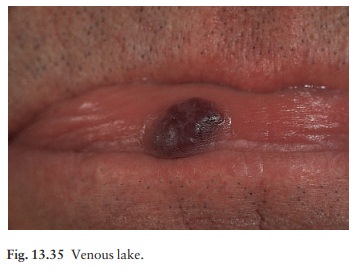
Venous lakes are blue or black
papules on the lips (Fig. 13.35). These melanoma-like lesions worry pati-ents
and doctors alike, but pressure with a diascope or glass slide causes them to
blanch.
•
Multiple, somewhat translucent,
papules may suggest Cowden’s syndrome. These are fibromas. Patients with
Cowden’s syndrome have facial papules and nodules (tricholemmomas and
fibromas), fibrocystic disease of the breasts and a great propensity to develop
malig-nant tumours of the breast, thyroid and other organs.
•
Patients with the multiple mucosal
neuroma syn-drome have neuromas in their mouths, and 75% of those with this
autosomal dominantly inherited dis-order also have medulary carcinoma of the
thyroid. Many also develop pheochromocytomas. Many small bumps appear along the
lips, tongue and buccal mucosae.
•
Pyogenic granulomas of the gingiva
appear as quick-growing red bleeding papules. They are reactive pro-liferations
of blood vessels, and often develop in pregnancy (‘pregnancy tumours’).
•
Fibromas may result from dentures,
or from resolving or indolent pyogenic granulomas, but can also appear without
reason, usually on the gingiva of adults. Tooth bites may cause fibromas to
appear on the tongue and on the buccal mucosae. Cowden’s disease should be considered if multiple lesions are
present.
• Warts in the mouth are not uncommon.
•
The differential diagnosis of oral
papules and nodules also includes lipomas, keloids, giant cell granulomas,
granular cell tumours, myxomas, xanthomas, hae-mangiomas, myomas, neural
tumours and a host of uncommon benign growths.
Related Topics