Chapter: An Introduction to Parallel Programming : Parallel Program Development
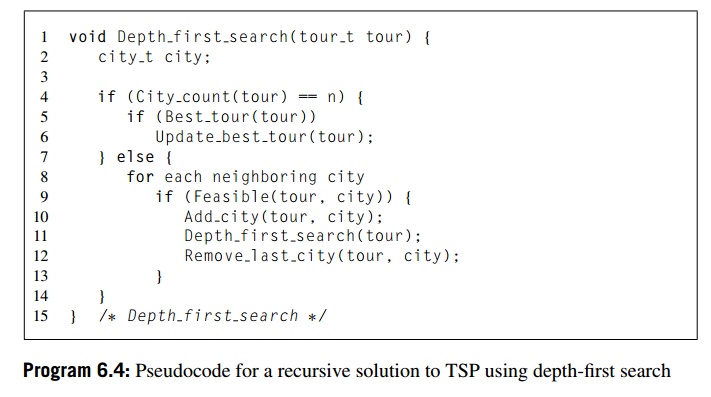
Recursive depth-first search
Recursive depth-first search
Using depth-first search we can systematically
visit each node of the tree that could possibly lead to a least-cost solution.
The simplest formulation of depth-first search uses recursion (see Program
6.4). Later on it will be useful to have a definite order in which the cities
are visited in the for loop in Lines 8 to 13, so we’ll assume that the cities are visited
in order of increasing index, from city 1 to city n-1.
The algorithm makes use of several global
variables:
. n: the total number of cities in the problem
. digraph: a data structure representing the
input digraph
. hometown: a data structure representing
vertex or city 0, the salesperson’s hometown
. best tour: a data structure representing the
best tour so far
The function City_count examines the partial
tour tour to see if there are n cities on the partial tour. If there are, we
know that we simply need to return to the hometown to complete the tour, and we
can check to see if the complete tour has a lower cost than the current “best_tour”
by calling Best tour. If it does, we can replace the current best tour with
this tour by calling the function Update_best-tour. Note that before the first
call to Depth_first_search, the best_tour variable should be initialized so
that its cost is greater than the cost of any possible least-cost tour.
If the partial tour tour hasn’t visited n
cities, we can continue branching down in the tree by “expanding the current
node,” in other words, by trying to visit other cities from the city last
visited in the partial tour. To do this we simply loop through the cities. The
function Feasible checks to see if the city or vertex has already been visited,
and, if not, whether it can possibly lead to a least-cost tour. If the city is
feasible, we add it to the tour, and recursively call Depth_first_search. When
Related Topics