Chapter: Mechanical : Maintenance Engineering : Maintenance Policies and Preventive Maintenance
Program Evaluation Review Techniques (PERT)
Scheduling
Techniques
Scheduling
is one of the areas that received considerable attention from researchers as well
as practitioners in all types of applications including operations scheduling
and project scheduling. Techniques are developed to develop optimum or near
optimal schedules with respect to different possible performance measures. This
chapter highlights some of these techniques and their application in
maintenance scheduling.
Program
Evaluation Review Techniques (PERT)
Maintenance
activities are usually unique and commonly involve unexpected needs that make
their time duration highly uncertain. CPM uses a single estimate of the time
duration based on the judgment of a person. PERT, on the other hand,
incorporates the uncertainty by three time estimates of the same activity to
form a probabilistic description of their time requirement. Even though the
three time estimates are judgmental they provide more information about the
activity that can be used for probabilistic modeling. The three values are
represented as follows:
Oi = optimistic time, which is the time required
if execution goes extremely well;
Pi = pessimistic time, which is the time required
under the worst conditions;
and
mi = most likely time, which is the time required
under normal condition.
The
activity duration is modeled using a beta distribution with mean ( ) and
variance ( ) for each activity i estimated from the three points as follows:
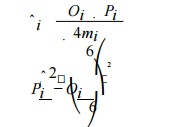
Estimated means are then used to find the critical path in the
same way of the CPM method. In PERT, the total time of the critical path is a
random variable with a value that is unknown in advance. However, additional
probabilistic analysis can be conducted regarding possible project durations
based on the assumption that the total time of the project may be approximated
by a normal probability
distribution
with mean and variance 2
estimated as
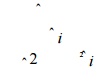
Using the
above approximation we can calculate the probability with which a project can
be completed in any time duration, T, using the normal distribution as follows:
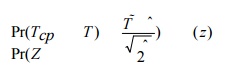
Where Φ is the
distribution function of the standard normal distribution.
Tables exist for evaluating any
probability under the standard normal distribution. To illustrate the PERT
analysis, consider the previous example with additional time estimates shown in
Table 11.7 below.
Table
11.7. The PERT calculation for the bearing overhaul example
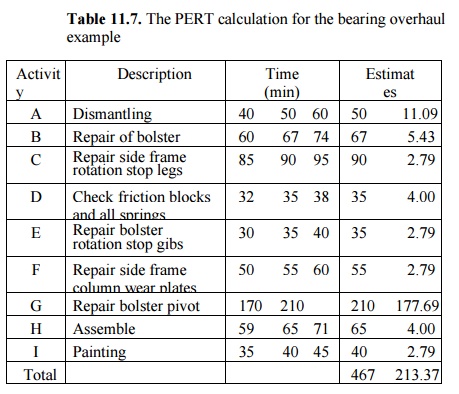
The
critical path calculations lead to the same critical path obtained in the
previous CPM calculations. The total project time is expected to be 467 min.
The estimated variance is 213.37 min. The probability that the project will
complete in
467
min can be calculated from the standard normal distribution to be
0.5,
or the project has a 50% chance
of completing in
467 min.
The probability that the project may
finish in 500 min
can be calculated as:
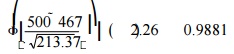
Related Topics