Chapter: Mechanical : Maintenance Engineering : Maintenance Policies and Preventive Maintenance
Lubrication
Lubrication
·
A Necessary Function
All material surfaces, no matter how smooth they
are, show many irregularities in the form of peaks and valleys, which are large
when considered on a molecular scale.
When these two solid surfaces are pressed over or
slide over each other, a real contact between these surfaces occurs that will
cause friction and consequently the production of heat. During the motion of
the sliding surfaces, a considerable amount of frictional heat is evolved at
the rubbing surface. This results in high local temperature even under
relatively light loads and speeds. This friction also causes a lot of wear and
tear of the surfaces of the moving parts.
Even under small load, the local pressure at the
peaks of the metals may be sufficiently great to cause appreciable deformation
in ductile metals. If two materials of different hardness slide over one
another, the peaks of the softer metal get broken more easily than the peaks of
the harder metals.
Lubrication reduces friction between the moving
surfaces or rolling pairs. The lubricant![]() also acts as a coolant carrying
heat away from the sliding surfaces, so proper lubrication of all the moving
parts is an important function in machinery or engine operation. By lubrication
we keep the moving surfaces separated by a fluid of some defined property
also acts as a coolant carrying
heat away from the sliding surfaces, so proper lubrication of all the moving
parts is an important function in machinery or engine operation. By lubrication
we keep the moving surfaces separated by a fluid of some defined property
·
Types of Lubrication
Considering the nature of motion between moving or
sliding surfaces, there are different types of mechanisms by which the
lubrication is done. They are:
· Hydrodynamic lubrication
or thick film lubrication
· Hydrostatic lubrication
· Boundary lubrication or
thin film lubrication
· Extreme pressure
lubrication
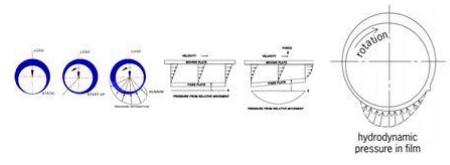
Hydrodynamic Lubrication or Thick Film Lubrication
Hydrodynamic lubrication is said to exist when the
moving surfaces are separated by the pressure of a continuous unbroken film or
layer of lubrication. In this type of lubrication, the load is taken completely
by the oil film.
The basis of hydrodynamic lubrication is the
formation of an oil wedge. When the journal rotates, it creates an oil taper or
wedge between the two surfaces, and the pressure build up with the oil film
supports the load.
Hydrodynamic lubrication depends on the relative speed between
the surfaces, oil viscosity![]() , load, and clearance between the
moving or sliding surfaces.
, load, and clearance between the
moving or sliding surfaces.
In hydrodynamic lubrication the lube oil film
thickness is greater than outlet, pressure at the inlet increases quickly,
remains fairly steady having a maximum value a little to the outside of the
bearing center line, and then decreases quickly to zero at the outlet.
Application
of hydrodynamic lubrication
· Delicate
instruments.
· Light
machines like watches, clocks, guns, sewing machines.
· Scientific
instruments.
· Large
plain bearings like pedestal bearings, main bearing of diesel
engines.
Hydrocarbon oils are
considered to be satisfactory lubrication for fluid film lubrication. In
order to maintain the viscosity of the oil in all seasons of the year, ordinary
hydrocarbon lubricants are blended with selected long chain polymers.
Hydrodynamic Lubrication
lubrication system is very important in diesel
engines.Lubrication reduces friction between the moving surfaces or rolling
pairs. various types of lubrication like hydrodynamic lubrication, hydrostatic
lubrication, boundary lubrication which are used in diesel engines are
explained in this article .
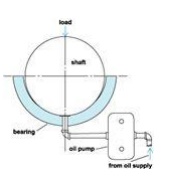
Hydrostatic Lubrication
Hydrostatic lubrication is essentially a form of
hydrodynamic lubrication in which the metal surfaces are separated by a
complete film of oil, but instead of being self-generated, the separating
pressure is supplied by an external oil pump. Hydrostatic lubrication depends
on the inlet pressure of lube oil and clearance between the metal surfaces,
whereas in hydrodynamic lubrication it depends on the relative speed between
the surfaces, oil viscosity, load on the surfaces, and clearance between the
moving surfaces.
Example: the cross head pin bearing or gudgeon pin bearing in
two stroke engines employs this hydrostatic lubrication mechanism. In the cross
head bearing, the load is very high and the motion is not continuous as the
bearing oscillation is fairly short. Thus hydrodynamic lubrication cannot be
achieved. Under such conditions, hydrostatic lubrication offers the advantage.
The oil is supplied under pressure at the bottom of bearing. The lube oil pump
pressure is related to the load, bearing clearance, and thickness of the oil
film required, but is usually in the order of 35-140 kg/cm2 .
Boundary Lubrication or Thin Film Lubrication
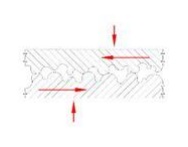
Boundary lubrication exists when the operating
condition are such that it is not possible to establish a full fluid condition,
particularly at low relative speeds between the moving or sliding surfaces.
The oil film thickness may be reduced to such a
degree that metal to metal contact occurs between the moving surfaces. The oil
film thickness is so small that oiliness becomes predominant for boundary
lubrication.
Boundary
lubrication happens when
· A shaft
starts moving from rest.
· The speed
is very low.
· The load
is very high.
· Viscosity
of the lubricant is too low.
Examples
for boundary lubrication:
· Guide and
guide shoe in two stroke engine.
· Lubrication
of the journal bearing in diesel engines (mainly during starting
and
stopping of engine).
· Piston
rings and when cylinder liner is at TDC and BDC position when the
piston
direction changes and if the relative speed is very slow.
Boundary Lubrication
Extreme Pressure
Lubrication
When the
moving or sliding surfaces are under very high pressure and speed, a high local
temperature is attained. Under such condition, liquid lubricant fails to stick
to the moving
parts and may decompose and even vaporize. To meet this extreme pressure condition, special additives are added to the minerals oils. These are called “extreme pressure lubrication.” These additives form on the metal surfaces more durable films capable of withstanding high loads and high temperature. Additives are organic compounds like chlorine (as in chlorinated esters), sulphur (as in sulphurized oils), and phosphorus.
Related Topics