Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Home Science Maintain Basic Knowledge for family life Higher secondary school College
Principles of House Design
Principles of Design
In our daily life, we meet with a number of designs. It is always
important to remember that beauty is the goal toward which we are striving for.
Utility also plays a major role in forming a good design. The following art principles are the bases for
judging good design. They are Harmony, Balance, Proportion, Rhythm, and
Emphasis.
Harmony
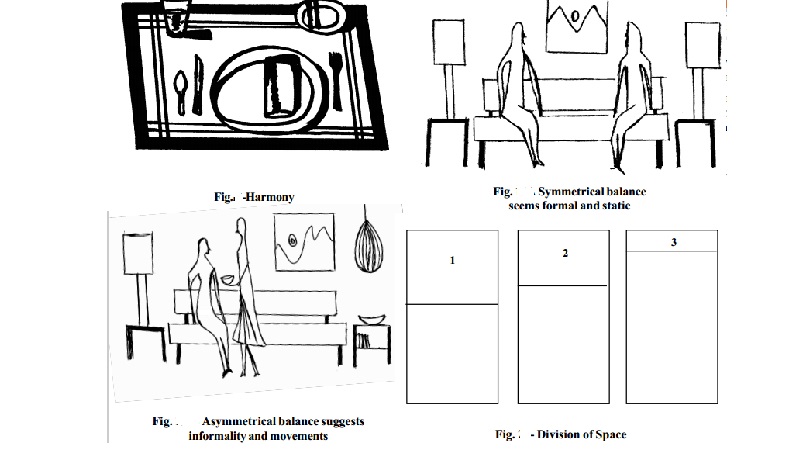
Harmony is the fundamental requirement of any piece of work. It means unity or a single idea or impression.
It produces an impression of unity through its selection and arrangement of
consistent objects and ideas. Forms, lines, textures and colours should be
harmonious.
For example, In a formal dinner arrangement, a table should have table
mats, plates, knives, spoons, forks, cups, hand towels etc., arranged in order
so as to achieve harmony of ideas. In a round plate, a round design will be
more apt than a square design.
Balance
Balance is equalization of attraction
on both sides of the center. It
is rest or repose. This effect is obtained by grouping shapes and colours around a center in such a
way that there are equal attractions on each side of that center.
Balance is of two
types
They are formal and informal balance.
Symmetrical or formal
balance results when articles are kept at equal distance. If objects are
similar in appearance, they will attract the same amount of attraction and
therefore should be equidistant from the center.
A design which has formal balance gives a feeling of dignity and
stateliness. Asymmetrical or informal
can have many variations. If the objects do not have the same amount of
attraction they must be placed at different distances from the center.
This type of the balance is just like see-saw, in which to balance off a
heavier person, the lighter one moves away from the centre and the former
towards the centre.
Informal balance is more creative and require much more effort than the
formal one. It gives an impression of spontaneity, freedom of movement and
casualness.
Proportion
Proportion means the relationship
of sizes or areas to one another or
to a whole. Whenever two or more things
are put together, good, or bad proportions are established. Proportion is
achieved when the different sizes of objects are successfully grouped in an
arrangement the elements making up the structure having a pleasing relationship
for the whole and to one another. For example, a very small chair next to a
very massive one would be 'out of scale'.
Greek oblong or Golden
Oblong is a good proportion, which can be used for division of space interestingly. This oblong
uses the ratio of 2:3 or 3:5 in case of flat surfaces and 5:7:11 in case of
solids. In the figures, three rectangles are given where the entire area is
divided into two portions. The division of the area can either be interesting
or uninteresting proportions. In A, the division is too simple to be
interesting. In C, the proportion is too unlike. In B, the divisions are
pleasantly related because they are little alike. The difference in the
division makes it interesting.
Rhythm
Rhythm is the movement of the
eyes across a design. It is a kind of organised and related movement in
continuity. Rhythm means an easy connected path along which the eye may travel
in any arrangement of line, form or colour. In a perfectly plain surface, there
is absolutely no movement of the eye and it remains quiet. Some line movements
create rhythm and others create a feeling of confusion.
Rhythm can be achieved
in many ways :
Through the repetition
of shapes
When a shape is regularly repeated at proper intervals, a movement is
created which carries the eye from one unit to the next.
Through a progression
of sizes
Progressing sizes create a rapid movement and at the same time
interesting.
Through an easily
connected, or a continuous line movement.
The eye is led along the design by the continuous line movement.
Radiation
Radiation is the plan for many geometric design. From a central point,
line radiate. Radiation is a type of movement that grows out of a central point
or axis. It is used very commonly in designs like Ashoka Chakra in the national
flag, and flower arrangements.
Emphasis
Emphasis is the art principle by which the eye is carried first to the
most important thing in any arrangement and from that point to every other
detail in order of importance.
Emphasis can be
achieved by the following ways
By placing or grouping of objects.
By the use of contrast of colour.
By using decoration.
By having sufficient background space around
objects.
By contrasting or unusual lines, shapes or
sizes.
By unusual texture.
So far we have learnt about the use of art principles in decorating the
interiors. Now we will learn about the different ways of furnishing the house.
Furniture for the
House
Furniture are pieces intended for comfort, rest and relaxation, storage
or articles of beauty. Furniture in all houses, are indispensable and they
provide for a harmonious living. While selecting furniture the following points
are to be borne in mind.
Furniture used should be in proportion to the
size of the room.
The design should be simple, plain, well constructed and provide comfort
to the user.
The furniture we select should be easy to
maintain.
The furniture should not occupy too much space.
It should be light weighted.
Children's furniture should be of adjustable
height (legs).
The furniture should be movable.
The furniture should be functional and not too
decorative.
The furniture should stand firmly.
General Rules
Select, a centre of interest and subordinate all other interests to it.
Observe balance in arrangement. Formal balance gives dignified, restful
effect, but too much of formal balance in a room will give a monotonous
appearance.
Retain good proportion while arranging. Place all large pieces on large
wall area and small pieces on small wall area.
Avoid using too many furniture in a room.
Scatter upholstered pieces among wooden pieces.
Avoid letting furniture hide the walls. But at the same time avoid
filling too much of the centre floor area. Keep the traffic lines in the room
very clear while arranging. Arrange all furniture with purpose and function in
mind, grouping those, which are needed for a particular activity in one place.
In the distribution of furniture, the housewife should exercise three
policies: elimination, re-arrangement,
and concealment. If one can afford, broken and unwanted furniture may be
discarded and fresh ones replaced. Furniture in a room may be reorganised so as
to achieve satisfaction. Unsightly and jarring object must be concealed by the
use of slipcovers. Defective and unattractive furniture can be concealed by the
use of good attractive covers.
Furniture Needed in
Different Rooms
Drawing Room: One comfortable sofa and few chairs.
Teapoy which is a bit lower than the seat of the sofa, television, video
cassette recorder, radio and record player cabinets to keep record albums.
Dining Room: Dining table and chairs, folding chair, if needed a trolley.
Bed Room: A double bed, bedside table and a lamp, dressing table, bed time table with lamp, place for suitcases, chairs.
Children's Room: A study table, a bed, book shelf.
Guest Room: Sofas which can be converted to bed.
Dressing table, bed side table with lamp, place for suitcases, chairs.
Kitchen: Built in storage space (appliances), stools, shelves, plate rack.
Related Topics