Chapter: Basic Electrical and electronics : Electrical Mechanics
Principles of DC motor Operation
DC MOTOR - INTRODUCTION
A machine
that converts dc power into mechanical energy is known as dc motor. Its
operation is based on the principle that when a current carrying conductor is
placed in a magnetic field, the conductor experiences a mechanical force. The
direction of the force is given by
Fleming’s
left hand rule.
How DC motors work?
There are
different kinds of D.C. motors, but they all work on the same principles.When a
permanent magnet is positioned around a loop of wire that is hooked up to a
D.C. power source, we have the basics of a D.C. motor. In order to make the
loop of wire spin, we have to connect a battery or DC power supply between its
ends, and support it so it can spin about its axis. To allow the rotor to turn
without twisting the wires, the ends of the wire loop are connected to a set of
contacts called the commutator, which rubs against a set of conductors called
the brushes. The brushes make electrical contact with the commutator as it
spins, and are connected to the positive and negative leads of the power
source, allowing electricity to flow through the loop. The electricity flowing
through the loop creates a magnetic field that interacts with the magnetic
field of the permanent magnet to make the loop spin.
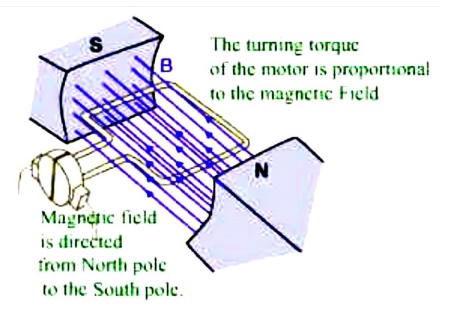
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
It is
based on the principle that when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a
magnetic field, it experiences a mechanical force whose direction is given by
Fleming's Left-hand rule and whose magnitude is given by
Force, F
= B I l newton
Where B
is the magnetic field in weber/m2. I is the current in amperes and
l is the
length of the coil in meter.
The
force, current and the magnetic field are all in different directions.
If an
Electric current flows through two copper wires that are between the poles of a
magnet, an upward force will move one wire up and a downward force will move
the other wire down.
BACK OR COUNTER EMF
When the
armature of a d.c. motor rotates under the influence of the driving torque, the
armature conductors move through the magnetic field and hence an e.m.f. is
induced in them. The induced e.m.f. acts in opposite direction to the applied
voltage V(Lenz’s law) and is known as back orcounter e.m.f. Eb.
SIGNIFICANCE OF BACK E.M.F
The
presence of back e.m.f. makes the d.c. motor a self-regulating machine i.e., it
makes the motor to draw as much armature current as is just sufficient to
develop the torque required by the load. Back e.m.f. in a d.c. motor regulates
the flow of armature current i.e., it automatically changes the armature
current to meet the load requirement.
Related Topics