Chapter: Basic Electrical and electronics : Electrical Mechanics
Important Short Questions and Answers: Basic Electrical Mechanics
ELECTRICAL MECHANICS
1. What is an electric generator?
An electrical machine, which converts mechanical
energy into electrical Energy, is called as electric generator.
2. What is an electric motor?
An electrical machine, which converts electrical
energy into mechanical Energy, is called as electric motor.
3. What is meant by magnetic
flux?
The
magnetic lines of force existing around a magnet is called magnetic flux. It’s
unit is
Weber.
4. State faraday’s law of
electromagnetic induction.
Whenever
a conductor cuts the magnetic lines of force an emf is induced in it.
5. State Fleming’s Right hand
rule.
If three fingers of right hand, namely thumb, index
finger and middle finger are outstretched so that everyone of them is at right
angles with the remaining two, and the index finger is made to point in the
direction of lines of flux, thumb in the direction of the relative motion of
the conductor and the middle finger gives the direction of the induced emf in
the conductor.
6.What is the use of commutator?
A device is used in a dc generator to convert the
alternating emf into unidirectional emf is called commutator.
7.What is the function yoke?
It serves
the purpose of outermost cover of the dc machine. So that
the
insulating material get protected from harmful atmospheric elements like
moisture, dust and various gases like SO2, acidic fumes etc.
It
provides mechanical support to the poles.
8.What is the choice of material
for the following?
1.Yoke
2.pole 3.Field winding 4.Armature winding
1.Yoke:
It is
prepared by using cast iron because it is cheapest.
2.Pole:
It is
made up of cast iron or cast steel.
3.Field winding:
It is
made up of aluminium or copper.
4.Armatuer winding:
It is
made up of cast iron or cast steel.
9.What is the function of brush?
To collect
current from commutator and make it available to the stationary external
circuit.
10.Write down the emf equation for d.c generator.
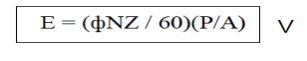
Where
P =
number of poles
Z = Total
number of conductors
A =
number of parallel paths
Ф = flux
per pole
N = speed
in rpm
11.What
are all the two types of excitation? i. Separate excitation
When the field winding is supplied from external, separate dc supply
i.e. Excitation of field winding is separate then the generator is called
separately excited generator.
ii. Self excitation
When the field winding is supplied from the armature of the generator
itself then it is called as self-excitation.
12.What is meant by residual magnetism?
Practically
though the generator is not working, without any current through field winding,
the field poles posses some magnetic flux. This is called as residual
magnetism.
13.Give the types of DC generator.
1.Self
excited generator
Series
Generator
Shunt
Generator Compound Generator
Long
shunt compound generator Short shunt compound generator
Cumulative
and differential compound Generator 2. Separately excited generator
14.List out the applications of various types of
generators.
Separately excited generator
As a
separate supply is required to excite the field, the use is restricted to some
special applications like electroplating, electro refining of materials etc
Shunt generator
Commonly
used in battery charging and ordinary lighting purposes.
Series Generators
Commonly
used as boosters on dc feeders, as a constant current generators for welding
generator and arc lamps.
Cumulatively compound generators
These are
used for domestic lighting purposes and to transmit energy over long distance.
Differential compound generator
The use
of this type of generators is very rare and it is used for special application
like electric arc welding.
15.what is the principle of DC motor?
Whenever
a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a
mechanical force.
16.State that the Fleming’s left hand rule.
The rules
states that outstretch the three fingers of the left hand namely the first
finger, middle finger and thumb such that they are mutually perpendicular to
each other. Now point the first finger in the direction of magnetic field and the
middle finger in the direction of the current then the thumb gives the
direction of the force experienced by the conductor.
17.What is Lenz’s law?
Lenz’s
law states the direction of induced emf is always so as to oppose the cause
producing it.
18.Give
the torque equation of a DC motor. Ta=0.159fIa.PZ/A N-m
Ia -
Armature current
P -
Number of poles
Z - Total
number of conductors
A -Number
of parallel paths
19.List the different types of DC motor.
DC series
motor
DC Shunt
motor
DC
Compound motor
Long
shunt compound motor
Short
shunt compound motor
20.List out the characteristics of DC motor.
i. Torque-Armature
current characteristics (T VS Ia)
ii. Speed-Armature
current characteristics (N VS Ia)
Blowers
and fans
Centrifugal
and reciprocating pumps
Lathe
machines
Machine
tools
Milling
machines
Drilling
machines
DC Series motor:
Cranes
Hoists,
Elevators
Trolleys,Conveyors,Electric
locomotives
DC Cumulative compound motor:
Rolling
mills
Punches
Shears
Heavy
planers
Elevators
22. How is voltage generated in rotating machines?
In
rotating machines voltage is generated in windings or group of coils by
rotating them through a magnetic field or by mechanically rotating a magnetic
field past the winding or by designing the magnetic circuit so that the
reluctance varies with rotation of the rotor.
23.What is the basic principle of dc motor?
A machine
that converts dc power into mechanical power is known as a dc motor its
operation is based on the principle that when a current carrying conductor is
placed in a magnetic field, the conductor experiences a mechanical force. The
direction of force is given by Fleming’s left hand rule and magnitude is given
by
F= BIL
netwons.
Basically
there is no constructional difference between a dc motor and dc generator. The
same dc machine can be run as a generator (or) motor.
24. What is back emf in d.c motors?
As the
motor armature rotates, the system of conductor come across alternate North and
South pole magnetic fields causing an emf induced in the conductors. The
direction of the emf induced in the conductors. The direction of the emf
induced is in the direction opposite to the current .As this emf always opposes
the flow of current in motor operation it is called back emf.
25. Mention the different parts of a d.c generator.
The
different parts of dc generator are
(i) Magnetic
frame (or) yoke.
(ii) pole core
and pole shoes
(iii) pole coil
or field coils
(iv)armature
windings or conductors
(v) armature
coils
(vi)commutator
(vii)Brushes
and bearing.
The
characteristics of DC generator are
i) no load
or saturation characteristics( Ea/ If)
ii) internal
characteristics(E/If)
iii) external
characteristics( V/If)
27.Write the various losses occurring in DC
generator
Copper
loss
Iron loss
Mechanical
loss
28. Mention the difference between core and shell
type transformers.
In core
type, the windings surround the core considerably and in shell type the core
surround the winding.
29. What is the purpose of laminating the core in a
transformer?
The
purpose of laminating the core in a transformer is to reduce eddy current loss.
30. Give the emf equation of a transformer and
define each term
Emf
induced in primary coil E1 = 4.44 fΦ mN1 volt
Emf
induced in secondary coil E2 = 4.44fΦ mN2 volt
Where f
is the frequency of AC input Φ m is the maximum value of flux in the core N1,
N2 are the number of primary and secondary turns.
31.Define voltage regulation of a transformer
When a
transformer is loaded with a constant primary voltage, the secondary voltage
decreases for lagging Power factor load, and increases for leading pf load
because of its internal resistance and leakage reactance. The change in
secondary terminal voltage from no load to full load expressed as a percentage
of no loads or full load voltage is termed as regulation.
% regulation
down = (0V2 -V2) x 100/0V2
% regulation
up = (0V2 -V2) x 100/V2
32.
Why
transformers are rated in kVA?
Copper
loss of a transformer depends on current and iron loss on voltage. Hence total
losses depend on Volt- Ampere and not on the power factor. That is why the
rating of transformers is in kVA and not in kW.
33.
What are
the typical uses of auto transformer?
(i)
To give small boost to a distribution cable to
correct for the voltage drop.
(ii)
As induction motor starters.
(iii)
As furnace transformers
(iv)
As interconnecting transformers
(v)
In control equipment for single phase and 3 phase
elective locomotives.
34.
When will
a Bucholz relay operate in a transformer?
Bucholz
rely is a protective device in a transformer.
If the
temperature of the coil exceeds its limit, Bucholz relay operates and gives an
alarm.
35. Why are breathers used in transformers?
Breathers
are used to entrap the atmospheric moisture and thereby not allowing it to pass
on to the transformer oil.
Also to
permit the oil inside the tank to expand and contract as its temperature
increases and decreases.
Nowadays
instead of natural mineral oil, synthetic oils known as ASKRELS (trade name)
are used. They are Noninflammable; under an electric arc do not decompose to
produce inflammable gases. PYROCOLOR oil possesses high dielectric strength.
Hence it
can be said that transformer oil provides,
(i)
good insulation and
(ii)
cooling.
37. An 1100/400 V, 50 Hz single phase transformer has
100 turns on the secondary winding. Calculate the number of turns on its
primary.
We know
V1 / V2 = k = N2 / N1 Substituting 400/1100 = 100/N1 N1 = 100/400 x 1100 = 275
turns.
38.
What are
the functions of no-load current in a transformer?
No-load
current produces flux and supplies iron loss and copper loss on no-load.
39. What is meant by a transformer?
The
transformer is a static piece of apparatus by means of which electrical power
is transformed from one alternating current circuit to another with desired
change in voltage and current. Without any change in the frequency. It works on
the principle of mutual induction .
40.
What are
the advantages of a transformer?
i)
Less I2R loss in the transmission line
ii)
Less voltage drop in the line
iii)
Efficiency of the transmission line is increased
iv)
Volume of the conductor required is less.
41.
What are
the properties of ideal transformer?
i) It has no
loss
ii) Its
winding have zero resistance.
iii) Leakage
flux is zero i.e 100% flux produced by primary links with the secondary
iv)Permeability
of core is so high that negligible current is required to establish the flues
is it.
40.
What are
the important parts of a transformer?
Transformer
consists of winding and magnetic core. The core is square or rectangle shape.
It consists of limb and yoke core is made up of lamination which is used to
reduce eddy current losses.
43. Define voltage transformation ratio?
The ratio
of secondary induced emf to primary induced emf is called as voltage regulation
ratio devoted by K.
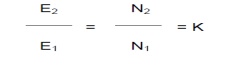
44.
Write the
expression for equivalent resistance and reactance of transformer referred to
primary.
Equivalent resistance Ro1 = R1 + R21 = R1 + R2/K2
Equivalent reactance Xo1 = X1 + X11 = X1
+ X2/K2
45.
Define
voltage regulations of a transformer.
The
decrease in secondary terminal voltage expressed as a fraction of the no load
secondary terminal voltage is called voltage regulation of a transformer.
46.
What are
the losses occurring in a transformer?
i) Core
losses
ii) Copper
losses
47.
What is
meant by core or iron losses?
Core or
iron losses are caused as the core gets subjected to an alternating flux.
48. What is meant by hysteresis losses?
Due to
alternating flux set up in the magnetic core of the transformer, it undergoes a
cycle of magnetization and demagnetization.
Due to
hysteresis effect there is loss of energy in this process which is called
hysteresis
loss.
49. What is meant by copper loss?
The
copper losses are due to the power wasted in the form of I2R due to the
resistances of the primary and secondary windings.
50. What is meant by eddy current loss?
The
induced emf in the core tries to set up eddy currents in the core and hence responsible
for the eddy current losses.
51.Define all day efficiency?
All day
efficiency is the ratio energy (in kwh) delivered in a 24 hours period to the
energy (in kwh) input for the same length of time.
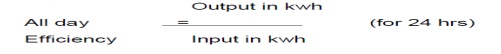
52. Define efficiency of a transformer?
The efficiency of a transformer is defined as the ratio of the output power to the input power.
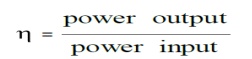
53. What is the function of capacitor in a single
phase induction motor?
Capacitor
is used to improve the power factor of the motor. Due to the capacitor
connected in series with the auxiliary winding, the capacitive circuit draws a
leading current which increases the split phase angle α between two phase
currents Im and Ist.
54. What is the use of shading coil in the shaded
pole motor?
In shaded
pole motors, the necessary phase-splitting is produced by induction. These
motors have salient poles on stator and a squirrel cage type rotor. The poles
are shaded i.e.; each pole carries a copper band one of its unequally divided part
called shading band.
When
single phase A.C. supply is given to the stator winding, due to shading
provided to the poles, a rotating magnetic field is generated.
55. Why capacitor-start induction motors
advantageous?
In
capacitor-start induction motors, capacitor is connected in series with the
auxiliary winding. When speed of the motor approaches to 75 to 80% of the
synchronous speed, the starting winding gets disconnected due to the operation
of the centrifugal switch. The capacitor remains in the circuit only at start.
The starting torque is proportional to phase angle α and hence such motors
produce very high starting torque.
56. List out four applications of shaded pole
induction motor?
Shaded
pole motors have very low starting torque, low power factor and low efficiency.
These motors are commonly used for small fans, toy motors, advertising
displays, film projectors, record players, gramophones, hair dryers, photo
copying machines etc.
57. What are the types of single phase induction
motors?
The types
of single phase induction motors are:
1. Split
phase induction motor.
2. Capacitor
start induction motor.
3. Capacitor
start and capacitor run motor.
4. Shaded
pole induction motor.
Related Topics