Chapter: Basic Electrical and electronics : Electrical Mechanics
Basic Equations and Applications of DC Motor
VOLTAGE EQUATION OF MOTORS
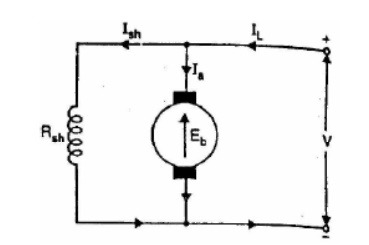
Let in a d.c. motor
V = applied voltage
Eb = back e.m.f.
Ra = armature resistance
Ia = armature current
Since
back e.m.f. Eb acts in opposition to the applied voltage V, the net voltage
across the armature circuit is V-Eb.
The
armature current Ia is given by
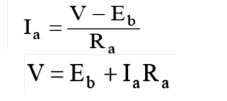
APPLICATIONS OF DC MOTORS:
1. D.C Shunt Motors:
It is a constant speed motor.Where the speed is required to
remain almost constant from noload to full load.Where the load has to be driven
at a number of speeds and any one of which is nearly constant.
Industrial use:
Lathes
Drills
Boring mills
Shapers
Spinning and Weaving machines.
2. D.CSeries motor:
It is a
variable speed motor.The speed is low at high torque.At light or no load ,the
motor speed attains dangerously high speed.The motor has a high starting
torque.(elevators,electric traction)
Industrial
Uses:
Electric
traction
Cranes
Elevators
Air
compressor
3. D.C Compound motor:
Differential
compound motors are rarely used because of its poor torque characteristics.
Industrial uses:
PressesShears
Reciprocating
machine.
CLASSIFICATION OF DC MOTOR
DC motors
are more common than we may think. A car may have as many as 20 DC motors to
drive fans, seats, and windows. They come in three different types, classified
according to the electrical circuit used. In the shunt motor, the armature and
field windings are connected in parallel, and so the currents through each are
relatively independent. The current through the field winding can be controlled
with a field rheostat (variable resistor), thus allowing a wide variation in
the motor speed over a large range of load conditions. This type of motor is
used for driving machine tools or fans, which require a wide range of speeds.
Related Topics