Chapter: 11 th 12th std standard Bio Botany plant tree Biology Higher secondary school College Notes
Plant Tikka disease in Groundnut or peanut - Arachis hypogea
Plant Tikka disease in Groundnut or peanut - Arachis hypogea
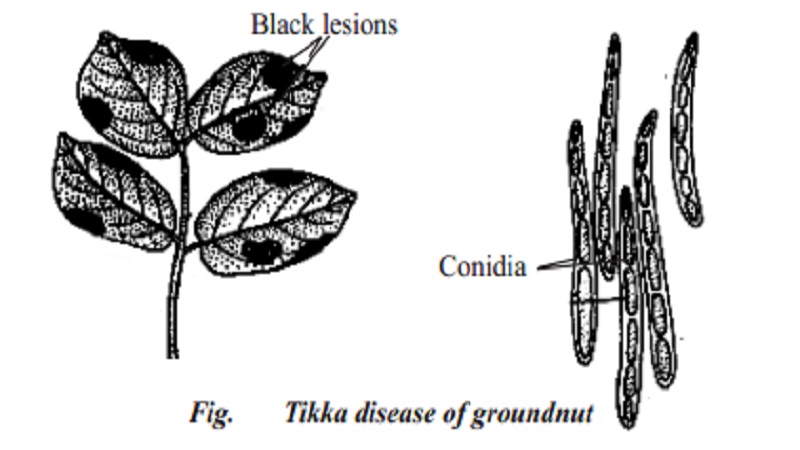
Tikka disease of groundnut
Pathogen : Disease incited by a fungus Cercospora personata.
Systematic position : The fungus belongs to class Deuteromycetes.
Symptoms
Lesions appear on the leaves, when the plants are atleast two months old. The symptoms appear in July and continue upto maturity of the plant. The lesions on the leaves are rounded and 1 to 6 mm in diameter.
These spots are dark brown or black and found on both surfaces of the leaf. Yellow border develops around each such leaf spot.
Pathogen
The mycelium of Cercospora personata is brown, septate branched and slender. Branched haustoria are produced to absorb food materials from the host tissue. The conidia are long and septate. Each conidiophore produces single conidium at its tip. The spread of the disease takes place by means of conidia which are dispersed by wind.
Control
The disease can be controlled by sanitation and crop rotation. The use of phosphatic and potassic manures reduce the disease. Sulphur dusting is quite effective. Resistant variety should be sown.
Crop diseases and their control
The diseases in crop plants result in a heavy loss of crop yields and cause considerable damage to crops year after year. To check the plant diseases, it becomes necessary to know about the cause of the diseases, of the life history of the causal organism and of the meterological conditions which influence the host and parasite interaction.
Control measures may be divided into two main groups - prophylaxis and disease resistance. Prophylaxis includes the protection of the host from exposure to the pathogen, from infection or from environmental factors favourable to disease development. Disease - resistance implies the improvement of resistance of the host to infection and to disease development.
Related Topics