Chapter: 11 th 12th std standard Bio Botany plant tree Biology Higher secondary school College Notes
Plant Respiration and structure of ATP
Plant Respiration
Light energy is converted into chemical energy and stored in complex organic molecules called carbohydrates - glucose and starch. The breaking of C - C bonds of such compounds through oxidation releases a considerable amount of energy. This energy is utilized for various metabolic activities at cellular level. This phenomenon of release of energy by oxidation of various organic molecules is known as respiration. The compounds that are oxidised during this process are known as respiratory substrates. Carbohydrate is the common respiratory substrate. During respiration, the whole energy contained in the respiratory substrate is not released all at once. In respiration, oxygen is utilized and carbondioxide, water and energy are released. Respiration is an exothermic reaction and the oxidation of glucose is given in the following equation.
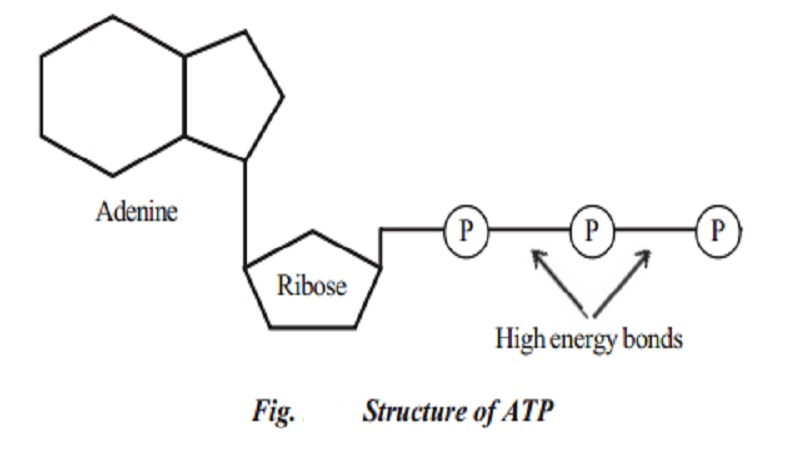
The energy released during this process is transformed into usable form of energy as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP molecules act as carriers of free energy between energy yielding and energy requiring reactions of the cell. Thus, ATP is described as energy currency of the cell. It is a nucloetide consisting of adenine, ribose sugar and three phosphate groups. It is an energy rich compound and contains two high energy terminal bonds. A large amount of free energy is liberated, when these bonds are broken by hydrolysis.
Related Topics