Chapter: 12th Statistics : Chapter 1 : Tests of Significance - Basic Concepts and Large Sample Tests
Parameter and Statistic
PARAMETER AND STATISTIC
A population, as described in Section 2.4 in XI Standard text book, is a
collection of units/objects/numbers under study, whose elements can be
considered as the values of a random variable, say, X. As mentioned in
Section 9.3 in XI Standard text book, there will be a probability distribution
associated with X.
Parameter: Generally, parameter is a quantitative characteristic, which indexes/identifies the respective
distribution. In many cases, statistical quantitative characteristics
calculated based on all the units in the population are the respective
parameters. For example, population mean, population standard deviation,
population proportion are parameters for some distributions.
Recall: The unknown constants
which appear in the probability density
function or probability mass function of the random variable X, are also called parameters of the corresponding distribution/population.
The parameters are commonly denoted by Greek letters. In
Statistical Inference, some or all the parameters of a population are assumed
to be unknown.
Random sample: Any set of reliazations (X1, X2 , ..., Xn) made on X under independent and identical conditions is
called a random
sample.
Statistic: Any statistical quantity calculated on the basis of the random
sample is called a statistic. The sample mean, sample standard deviation, sample proportion etc.,
are called statistics
(plural form of statistic).They will be
denoted by Roman letters.
Let (x1, x2, …, xn) be an
observed value of (X1, X2, ..., Xn).
The collection of (x1, x2, …, xn) is
known as sample space, which will be denoted by ‘S’.
Note 1
A set of n sample observations can be made on X, say, x1,
x2, …, xn for making inferences on the unknown
parameters. It is to be noted that these n values may vary from sample to
sample. Thus, these values can be considered as the realizations of the random
variables X1, X2, ..., Xn ,which are assumed
to be independent and have the same distribution as that of X. These are also
called independently and identically distributed (iid) random variables.
Note 2:
In Statistical Inference, the sample standard deviation is
defined as S = 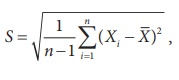 where
where 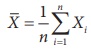 . It may be noted that the divisor is n
– 1 instead of n
. It may be noted that the divisor is n
– 1 instead of n
Note 3:
The statistic itself is a random variable, until the numerical
values of X1, X2, ..., Xn
are observed, and hence it has a probability distribution.
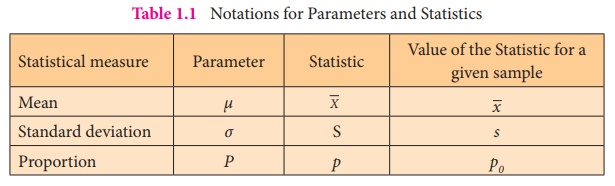
Notations to denote various population parameters and their
corresponding sample statistics are listed in Table 1.1. The notations will be
used in the first four chapters of this book with the same meaning for the sake
of uniformity.
Related Topics