Chapter: Aquaculture Engineering : Heating and Cooling
Oil and gas burners heaters - Aquaculture Engineering
Oil and gas burners
When oil burns a great deal of energy is released, and in
an oil burner this energy is used to heat water. The amount of energy released
when burning 1 l oil depends on the characteristics and quality of the oil; a
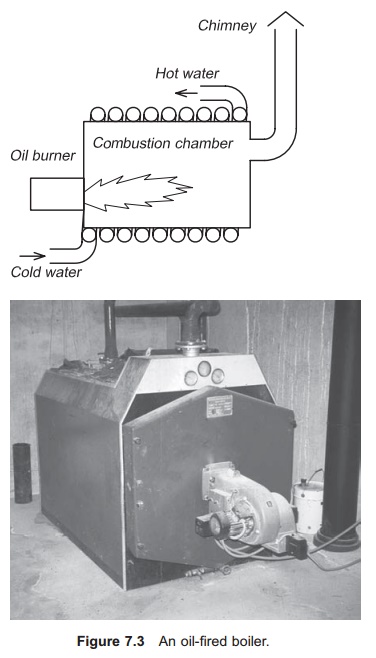
typical value is 41 800 kJ/kg. Letting the oil burn in a combustion chamber
around which water flows ensures transfer of energy from the burning oil to the
water (Fig. 7.3). To keep the oil burning, air must be supplied to the
combustion chamber and a chimney is necessary to get rid of the flue gas. There
will always be energy losses in an oil-fired boiler from the flue gas and due
to incomplete burning and incomplete transfer of heat to the water. Depending
on the system, oil-fired boilers are usually between 60 and 90% efficient. A
shunt valve may be used to regulate the temperature of the water flowing out
from an oil-fired boiler.
Instead of oil, gas can be used as an energy source. The
construction of a gas-fired system is similar to an oil-fired system, with a
combustion chamber around which the water circulates. However, the gas-fired
boiler is slightly simpler to construct, because gas is more flammable than
oil. Normally gas-fired appliances are slightly more efficient than oil-fired
boilers.
Related Topics